Formulation and Delivery - Chemical
(W1230-10-57) Efficient Development of High Drug-Loaded Posaconazole Tablets Enabled by Amorphous Solid Dispersion
Wednesday, October 23, 2024
12:30 PM - 1:30 PM MT

Tianyi Xiang, MS
Graduate Research Assistant
University of Minnesota
Minneapolis, Minnesota, United States
Tianyi Xiang, MS
Graduate Research Assistant
University of Minnesota
Minneapolis, Minnesota, United States
Sichen Song, Ph.D. (he/him/his)
Graduate Research Assistant
University of Minnesota
MINNEAPOLIS, Minnesota, United States- RS
Ronald Siegel, Sc.D.
Professor and Director of Graduate Studies
University of Minnesota
MINNEAPOLIS, Minnesota, United States 
Changquan Calvin Sun, Ph.D.
Professor and Associate Department Head
University of Minnesota
Minneapolis, Minnesota, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Main Author(s)
Co-Author(s)
Purpose: Amorphous solid dispersion (ASD) is an enabling technology for improving the dissolution and bioavailability of poorly water soluble drugs. However, drug loadings in ASD-based tablets are usually kept low ( < 20%) to ensure physical stability of the product, which leads to a large pill burden. Recent studies have shown that the overlap concentration of polymer in an ASD, c*, sets the upper limit of drug loading in an ASD to maintain physical stability12. Thus, the determination of c* is an excellent first step for efficiently developing an ASD-based high drug loaded tablet. In this work, we aim to demonstrate the potential of this strategy by efficiently developing an ASD-based high drug loaded tablet of posaconazole (POSA).
Methods: The thermal behaviors of neat POS and cryomilled physical mixtures of POS and hydroxypropyl methylcellulose acetate succinate (M grade) (HPMCAS) were studied by DSC. The viscosities of POSA-HPMCAS binary mixtures with various polymer concentrations were determined at 175 oC (above the melting temperature of POSA) using a rotational rheometer. A viscosity-composition diagram was constructed, from which c* was determined. Three ASD batches of various POSA loadings below the critical drug concentration, 1- c*, were prepared using a laboratory spray dryer. Powder dissolution was performed for these ASD batches in 0.1 M PBS (pH 6.5) at 37 ˚C. Flowability of powders was assessed by Carr’s compressibility index. Tablets and ribbons were compressed on a compaction simulator. True densities of powders were measured by a helium pycnometer. Tablet friability profiles were determined using a friability tester with an expedited method 3. Tablet dissolution was conducted in pH 6.5 PBS with 0.05% v/v Tween 20 at 37 ˚C, where a UV-Vis dip probe was used to monitor concentration in situ.
Results: The favorable interaction between POSA and HPMCAS was demonstrated by the depressed melting point of POSA in the 96% POSA + 4% HPMCAS physical mixture 4 (Fig. 1a). The c* of HPMCAS in molten POSA, determined from the viscosity-composition diagram 5, was 3% (Fig. 1b). Thus, physical stability of an ASD can be expected up to 97% POSA loading 5. However, among the ASDs with 60%, 70%, and 80% POSA loadings, only the 60% and 70% ASDs showed appreciable dissolution (Fig. 1c). The 70% ASD was therefore used to prepare a tablet formulation. The 70% POSA loaded ASD exhibited very poor flowability. To overcome the flowability problem, dry granulation was adopted. In the formulation (Table 1), 21.9% MCC PH101 was used as an intragranular binder for ribbon manufacturing due to the weak tabletability of the pure 70% POSA loaded ASD (Fig. 1d). 3% Ac-Di-Sol was added both intragranularly and extragranularly to facilitate disintegration of both tablets and granules during dissolution. The pre-granulation blend (intragranular) was compressed into simulated ribbons with 15% porosity under a pressure of 77 MPa. This pressure was identified from the experimentally determined compressibility profile of the pre-blend (Fig. 2a). Granules were obtained by milling ribbons and then blended with colloidal silica to further enhance flow and magnesium stearate to reduce ejection force. The final blend exhibited flowability meeting the criterion for high speed tableting 6 (Fig. 2b). The tablet friability profile, obtained using a material sparing and expedited approach, suggested that tablets with < 0.8% friability could be attained at a compaction pressure ≥ 100 MPa (Fig. 2c). Therefore, POSA tablets containing 50% POSA were compressed at 100 MPa. Such tablets exhibited a fast dissolution in PBS, similar to that of 70% POSA ASD powder (Fig. 2d).
Conclusion: By using material-sparing techniques, we successfully developed a 50% POSA loaded tablet exhibiting adequate manufacturability and good dissolution performance. This was achieved using only ~ 1.5 g of POSA. The identification of an upper limit of drug loading in ASD based on the c* concept was instrumental in guiding the materials-sparing tablet formulation strategy. Combined with assessing dissolution performance, this strategy ensures the efficient identification of maximum drug loading in an ASD-based tablet.
References: (1) Sahoo, A.; Suryanarayanan, R.; Siegel, R. A. Stabilization of Amorphous Drugs by Polymers: The Role of Overlap Concentration (C*). Mol. Pharm. 2020, 17 (11), 4401–4406.
(2) Song, S.; Yao, X.; Wang, C.; Sun, C. C.; Siegel, R. A. Delaying the First Nucleation Event of Amorphous Solid Dispersions above the Polymer Overlap Concentration (C*): PVP and PVPVA in Posaconazole. J. Pharm. Sci. 2024.
(3) Osei-Yeboah, F.; Sun, C. C. Validation and Applications of an Expedited Tablet Friability Method. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 484 (1), 146–155.
(4) Sun, Y.; Tao, J.; Zhang, G. G. Z.; Yu, L. Solubilities of Crystalline Drugs in Polymers: An Improved Analytical Method and Comparison of Solubilities of Indomethacin and Nifedipine in PVP, PVP/VA, and PVAc. J. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 99 (9), 4023–4031.
(5) Song, S.; Wang, C.; Zhang, B.; Sun, C. C.; Lodge, T. P.; Siegel, R. A. A Rheological Approach for Predicting Physical Stability of Amorphous Solid Dispersions. J. Pharm. Sci. 2023, 112 (1), 204–212.
(6) Chattoraj, S.; Shi, L.; Sun, C. C. Profoundly Improving Flow Properties of a Cohesive Cellulose Powder by Surface Coating with Nano‐silica through Comilling. J. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 100 (11), 4943–4952.
Acknowledgements: We thank the National Science Foundation for support through the Industry University Collaborative Research Center (IUCRC) grant IIP-2137264, Center for Integrated Materials Science and Engineering for Pharmaceutical Products (CIMSEPP).
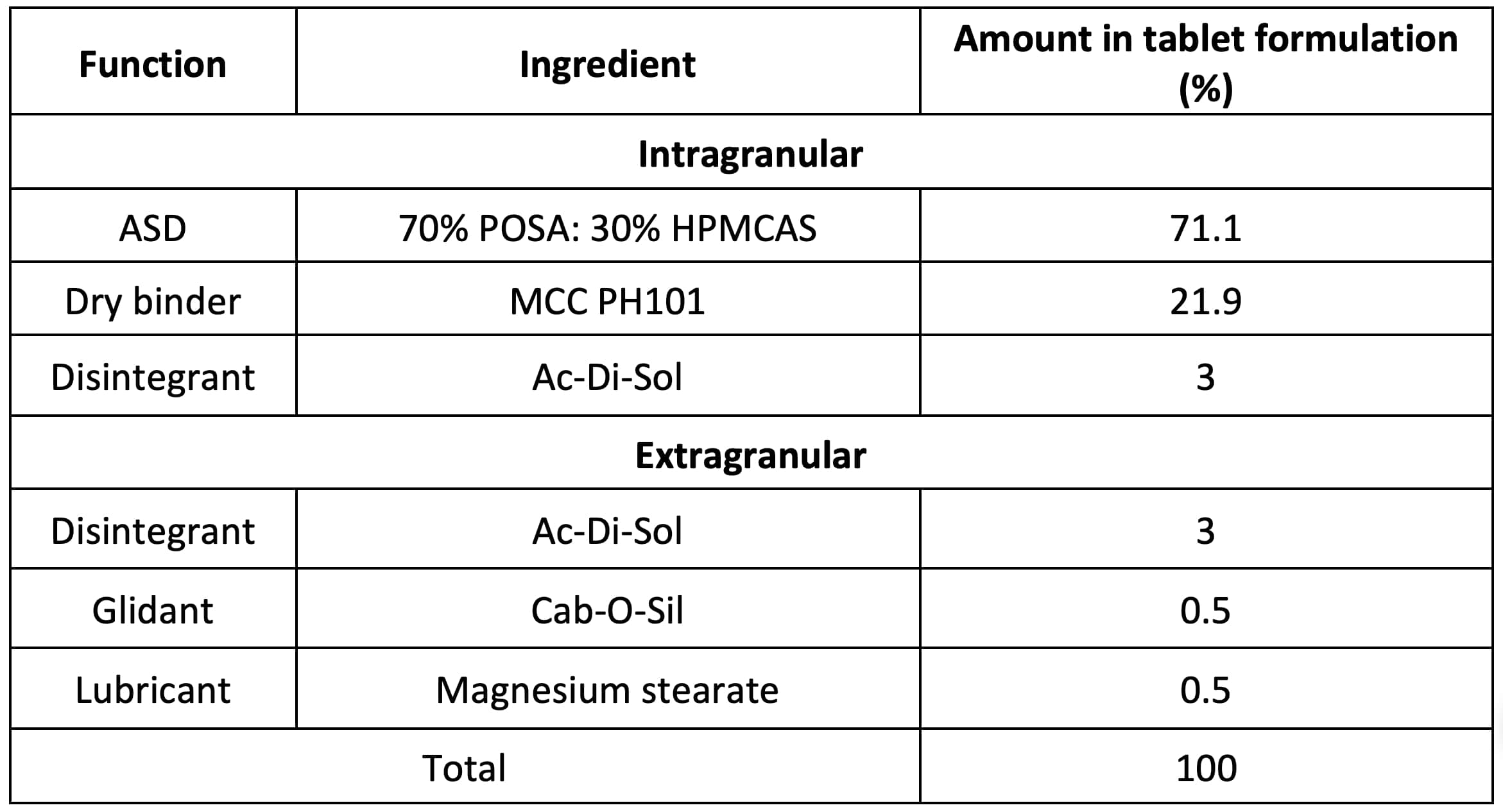 Table 1. Formulation of 50% drug-loading posaconazole tablet containing ASD of 70% posaconazole and 30% HPMCAS.
Table 1. Formulation of 50% drug-loading posaconazole tablet containing ASD of 70% posaconazole and 30% HPMCAS.
 Figure 1. a) DSC profiles of pure POSA (black) and its physical mixture with 4% HPMCAS (red), showing melting point depression. b) Viscosity-composition diagram of POSA and HPMCAS at 175 °C. c) Powder dissolution profiles of POSA - HPMCAS ASDs with 60%, 70%, and 80% POS loadings in 0.1 M PBS (pH 6.5) at 37 ˚C. d) Tabletability of powders in different stages of tablet formulation design.
Figure 1. a) DSC profiles of pure POSA (black) and its physical mixture with 4% HPMCAS (red), showing melting point depression. b) Viscosity-composition diagram of POSA and HPMCAS at 175 °C. c) Powder dissolution profiles of POSA - HPMCAS ASDs with 60%, 70%, and 80% POS loadings in 0.1 M PBS (pH 6.5) at 37 ˚C. d) Tabletability of powders in different stages of tablet formulation design.
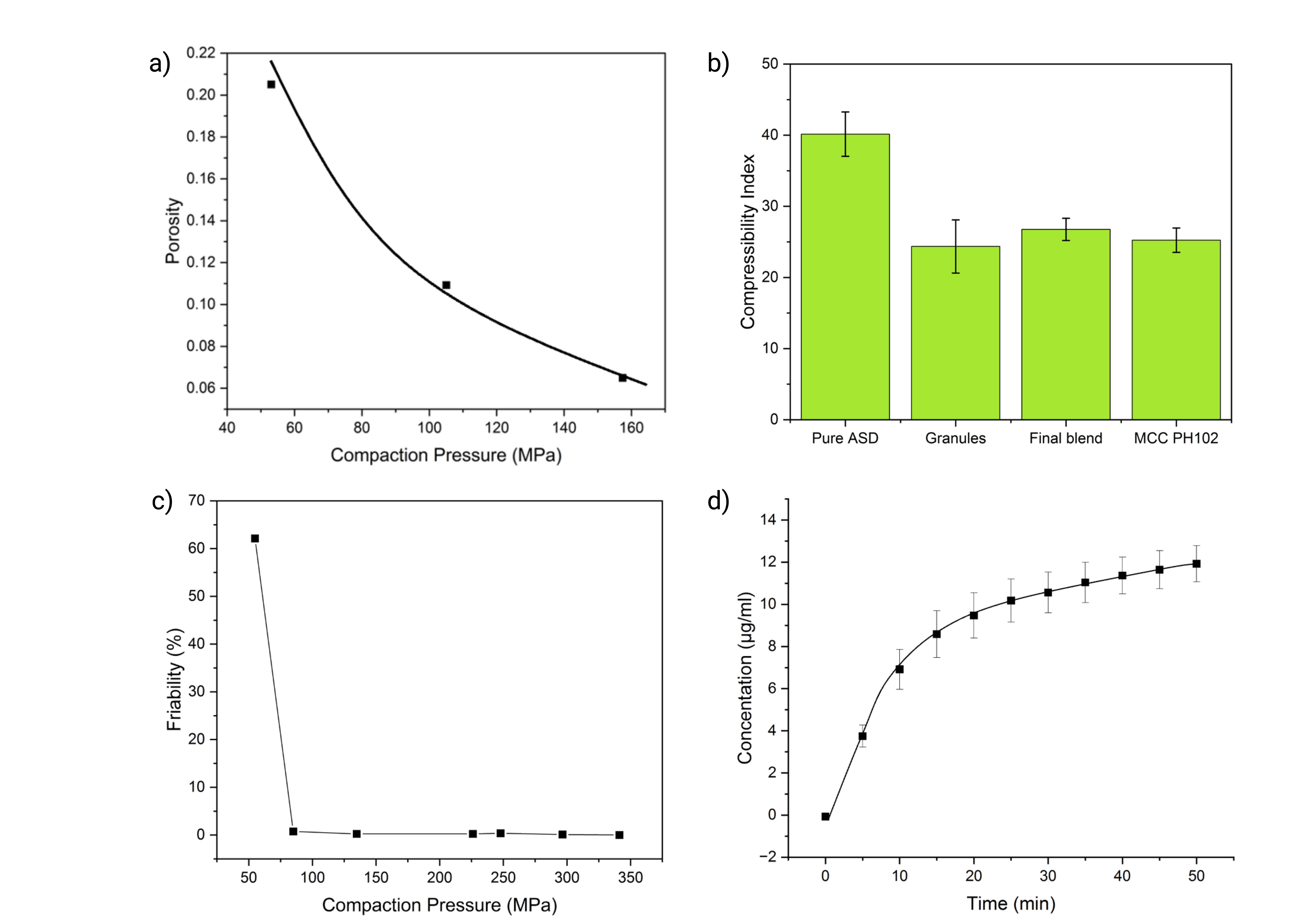 Figure 2. a) Compressibility profile of the pre-granulation blend. The line was obtained by fitting data with the Kuentz-Leuenberger (KL) equation. b) Flowability of powders in different stages of tablet formulation design assessed by Carr’s compressibility index. c) Friability profile of tablets containing 70% ASD. d) Time-concentration profile of dissolution of final tablets in pH 6.5 PBS with 0.05% v/v Tween 20 at 37 ˚C (non-sink condition, n = 3).
Figure 2. a) Compressibility profile of the pre-granulation blend. The line was obtained by fitting data with the Kuentz-Leuenberger (KL) equation. b) Flowability of powders in different stages of tablet formulation design assessed by Carr’s compressibility index. c) Friability profile of tablets containing 70% ASD. d) Time-concentration profile of dissolution of final tablets in pH 6.5 PBS with 0.05% v/v Tween 20 at 37 ˚C (non-sink condition, n = 3).
Methods: The thermal behaviors of neat POS and cryomilled physical mixtures of POS and hydroxypropyl methylcellulose acetate succinate (M grade) (HPMCAS) were studied by DSC. The viscosities of POSA-HPMCAS binary mixtures with various polymer concentrations were determined at 175 oC (above the melting temperature of POSA) using a rotational rheometer. A viscosity-composition diagram was constructed, from which c* was determined. Three ASD batches of various POSA loadings below the critical drug concentration, 1- c*, were prepared using a laboratory spray dryer. Powder dissolution was performed for these ASD batches in 0.1 M PBS (pH 6.5) at 37 ˚C. Flowability of powders was assessed by Carr’s compressibility index. Tablets and ribbons were compressed on a compaction simulator. True densities of powders were measured by a helium pycnometer. Tablet friability profiles were determined using a friability tester with an expedited method 3. Tablet dissolution was conducted in pH 6.5 PBS with 0.05% v/v Tween 20 at 37 ˚C, where a UV-Vis dip probe was used to monitor concentration in situ.
Results: The favorable interaction between POSA and HPMCAS was demonstrated by the depressed melting point of POSA in the 96% POSA + 4% HPMCAS physical mixture 4 (Fig. 1a). The c* of HPMCAS in molten POSA, determined from the viscosity-composition diagram 5, was 3% (Fig. 1b). Thus, physical stability of an ASD can be expected up to 97% POSA loading 5. However, among the ASDs with 60%, 70%, and 80% POSA loadings, only the 60% and 70% ASDs showed appreciable dissolution (Fig. 1c). The 70% ASD was therefore used to prepare a tablet formulation. The 70% POSA loaded ASD exhibited very poor flowability. To overcome the flowability problem, dry granulation was adopted. In the formulation (Table 1), 21.9% MCC PH101 was used as an intragranular binder for ribbon manufacturing due to the weak tabletability of the pure 70% POSA loaded ASD (Fig. 1d). 3% Ac-Di-Sol was added both intragranularly and extragranularly to facilitate disintegration of both tablets and granules during dissolution. The pre-granulation blend (intragranular) was compressed into simulated ribbons with 15% porosity under a pressure of 77 MPa. This pressure was identified from the experimentally determined compressibility profile of the pre-blend (Fig. 2a). Granules were obtained by milling ribbons and then blended with colloidal silica to further enhance flow and magnesium stearate to reduce ejection force. The final blend exhibited flowability meeting the criterion for high speed tableting 6 (Fig. 2b). The tablet friability profile, obtained using a material sparing and expedited approach, suggested that tablets with < 0.8% friability could be attained at a compaction pressure ≥ 100 MPa (Fig. 2c). Therefore, POSA tablets containing 50% POSA were compressed at 100 MPa. Such tablets exhibited a fast dissolution in PBS, similar to that of 70% POSA ASD powder (Fig. 2d).
Conclusion: By using material-sparing techniques, we successfully developed a 50% POSA loaded tablet exhibiting adequate manufacturability and good dissolution performance. This was achieved using only ~ 1.5 g of POSA. The identification of an upper limit of drug loading in ASD based on the c* concept was instrumental in guiding the materials-sparing tablet formulation strategy. Combined with assessing dissolution performance, this strategy ensures the efficient identification of maximum drug loading in an ASD-based tablet.
References: (1) Sahoo, A.; Suryanarayanan, R.; Siegel, R. A. Stabilization of Amorphous Drugs by Polymers: The Role of Overlap Concentration (C*). Mol. Pharm. 2020, 17 (11), 4401–4406.
(2) Song, S.; Yao, X.; Wang, C.; Sun, C. C.; Siegel, R. A. Delaying the First Nucleation Event of Amorphous Solid Dispersions above the Polymer Overlap Concentration (C*): PVP and PVPVA in Posaconazole. J. Pharm. Sci. 2024.
(3) Osei-Yeboah, F.; Sun, C. C. Validation and Applications of an Expedited Tablet Friability Method. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 484 (1), 146–155.
(4) Sun, Y.; Tao, J.; Zhang, G. G. Z.; Yu, L. Solubilities of Crystalline Drugs in Polymers: An Improved Analytical Method and Comparison of Solubilities of Indomethacin and Nifedipine in PVP, PVP/VA, and PVAc. J. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 99 (9), 4023–4031.
(5) Song, S.; Wang, C.; Zhang, B.; Sun, C. C.; Lodge, T. P.; Siegel, R. A. A Rheological Approach for Predicting Physical Stability of Amorphous Solid Dispersions. J. Pharm. Sci. 2023, 112 (1), 204–212.
(6) Chattoraj, S.; Shi, L.; Sun, C. C. Profoundly Improving Flow Properties of a Cohesive Cellulose Powder by Surface Coating with Nano‐silica through Comilling. J. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 100 (11), 4943–4952.
Acknowledgements: We thank the National Science Foundation for support through the Industry University Collaborative Research Center (IUCRC) grant IIP-2137264, Center for Integrated Materials Science and Engineering for Pharmaceutical Products (CIMSEPP).
 Table 1. Formulation of 50% drug-loading posaconazole tablet containing ASD of 70% posaconazole and 30% HPMCAS.
Table 1. Formulation of 50% drug-loading posaconazole tablet containing ASD of 70% posaconazole and 30% HPMCAS.  Figure 1. a) DSC profiles of pure POSA (black) and its physical mixture with 4% HPMCAS (red), showing melting point depression. b) Viscosity-composition diagram of POSA and HPMCAS at 175 °C. c) Powder dissolution profiles of POSA - HPMCAS ASDs with 60%, 70%, and 80% POS loadings in 0.1 M PBS (pH 6.5) at 37 ˚C. d) Tabletability of powders in different stages of tablet formulation design.
Figure 1. a) DSC profiles of pure POSA (black) and its physical mixture with 4% HPMCAS (red), showing melting point depression. b) Viscosity-composition diagram of POSA and HPMCAS at 175 °C. c) Powder dissolution profiles of POSA - HPMCAS ASDs with 60%, 70%, and 80% POS loadings in 0.1 M PBS (pH 6.5) at 37 ˚C. d) Tabletability of powders in different stages of tablet formulation design.  Figure 2. a) Compressibility profile of the pre-granulation blend. The line was obtained by fitting data with the Kuentz-Leuenberger (KL) equation. b) Flowability of powders in different stages of tablet formulation design assessed by Carr’s compressibility index. c) Friability profile of tablets containing 70% ASD. d) Time-concentration profile of dissolution of final tablets in pH 6.5 PBS with 0.05% v/v Tween 20 at 37 ˚C (non-sink condition, n = 3).
Figure 2. a) Compressibility profile of the pre-granulation blend. The line was obtained by fitting data with the Kuentz-Leuenberger (KL) equation. b) Flowability of powders in different stages of tablet formulation design assessed by Carr’s compressibility index. c) Friability profile of tablets containing 70% ASD. d) Time-concentration profile of dissolution of final tablets in pH 6.5 PBS with 0.05% v/v Tween 20 at 37 ˚C (non-sink condition, n = 3).