Discovery and Basic Research
(T1130-06-31) ML-Driven Multi-Omics Analysis of Platelet-Rich Plasma: Differentiating Age-Related Biomarkers in Young and Old Individuals

Hugo Gagnon, PhD
CSO
Allumiqs
Sherbrooke, Quebec, Canada
Hugo Gagnon, PhD
CSO
Allumiqs
Sherbrooke, Quebec, Canada- JN
Jean-Francois Noel, Ph.D.
Sr. Scientific manager
Allumiqs
Sherbrooke, Quebec, Canada - SP
Simon Perrin, Ph.D.
Sr. Scientist
Allumiqs
Sherbrooke, Quebec, Canada - JN
Jessica Nickerson, Ph.D.
Scientist
Allumiqs
Sherbrooke, Quebec, Canada - VM
Victoria Milller, Ph.D.
Scientist R&D manager
Allumiqs
Sherbrooke, Quebec, Canada - AA
Ariss Alimi, MS
ML and Bioinformatics Scientist
Simmunome Inc.
montreal, Quebec, Canada - NN
Nardin Nakhla, Ph.D.
CTO
Simmunome Inc.
montreal, Quebec, Canada - AM
Armstrong Murira, Ph.D.
CEO
Simmunome Inc.
montreal, Quebec, Canada - AC
Anik Chevrier, Ph.D.
Research associate
Polytechnique Montreal
Monteral, Quebec, Canada - ML
Marc Lavertu, Ph.D.
Associate Professor
Polytechnique Montréal
Montreal, Quebec, Canada
Presenting Author(s)
Main Author(s)
Co-Author(s)
Methods: Sixty patients aged 18-63 were recruited, divided into “young” ( < 40 years, n=45) and “old” (≥40 years, n=15) groups. PRP was extracted via freeze-thaw method, and multiomic profiling was performed using LC-MS/MS. Proteomics data were acquired using Data Independent Acquisition (DIA), and metabolomics using the biocrates AbsoluteIDQ® p400 HR kit. Following data normalization, low-quality feature removal, and missing value imputation, we quantified 731 protein groups and 200 lipids/metabolites. Feature selection methods (K-best, Random Forest, Boruta, and Lasso) were evaluated for their precision and accuracy in classifying PRP samples using machine learning (ML) classifier i.e. RandomForest (RF) and support vector machine (SVM) models.
Results: When using unsupervised clustering methods, both features driven and network/graph based driven, we were able to segregate clusters of patients. However, this cluster did correspond to any of the metadata available including sex and age. We next tested RF classifier and SVM classifier on the whole dataset. Using train/test group permutation, we were able to obtain 89% prediction of young PRP on average, but prediction of old PRP had an average score of .69 with some prediction failing. RF failed in most cases to predict old PRP. We thus evaluated the effect of features selection methods and on precision, accuracy and stability of the model following permutation analysis. We also evaluate the effect of the number of selected features when available to the selection method. Lasso (a linear regression regularization method) performed the best by selecting 20 features leading to good prediction with both RF (ROC AUC of.98, with a tightly distributed precision and recall above .9) and SVM model (ROC AUC of 1 with precision and recall above .9 in most of the case, but higher variability than RF model). Interestingly, k_best and Boruta selected features model performance decreased while increasing the number of selected features. MRMR method worked best in conjunction with SVM and 100 selected features but still underperformed other methods with ROC AUC of .95 precision and recall between .8 and .9 with a very high standard deviation) . The worst method in general was permutation importance. Interestingly, all features selection method ended with a combination of protein and metabolite, supporting the utility of multiomics approach. While this approach is key for biomarker-based approach, we wanted to evaluate if the approach can also be useful for knowledge extraction using GO and network analysis of selected features. To determine if a method would be best regarding knowledge extraction, we have evaluated the GO and network function of lasso-RF model, Boruta-SVM with mid-stringency features selection and MRMR-SVM model with 200 features. We show that using a less robust model with more features help drawing conclusions regarding pathway analysis, but that more stringent features selection methods still tend to keep key candidates of a protein family, opening an avenue for a different approach that could use features reductions prior to features selection.
Conclusion: Using ML-driven analysis, we identified several key proteins and metabolites capable of differentiating between young and old PRP samples. Omics data combined with machine learning approaches revealed distinct proteomic and metabolomic profiles in young versus old PRP. The proposed approach identified biomarkers could enhance understanding of PRP's age-related therapeutic potential, guiding more effective clinical applications. We also propose that the processed used in this study can be replicated on other disease and treatment to help de-risk drug development and help contextualize preclinical models to clinical data.
References: 1-Rossi L, Ranalletta M, Pasqualini I, Zicaro JP, Paz MC, Camino P, Piuzzi NS. Substantial Variability in Platelet-Rich Plasma Composition Is Based on Patient Age and Baseline Platelet Count. Arthrosc Sports Med Rehabil. 2023 May 20;5(3):e853-e858. doi: 10.1016/j.asmr.2023.03.017. PMID: 37388884; PMCID: PMC10300586.
Acknowledgements:
Funding: This project was funded by CQDM-Partnar-AI with financial contribution of MITACS, allumiqs,Simmunome and Chitogenx.
Acknowledgement: We would like to thank ChitogeneX for their contribution to this project.
Disclosure: Hugo Gagnon is director and shareholder at Allumiqs, Armstrong Murira and Nardin Nakhla are directors and shareholders at Simmunome.
Ethics approvals: Samples were collected under a Ethic protocol approved by Comité d'éthique à la recherche avec des êtres humains of Polytehcnique Montreal.
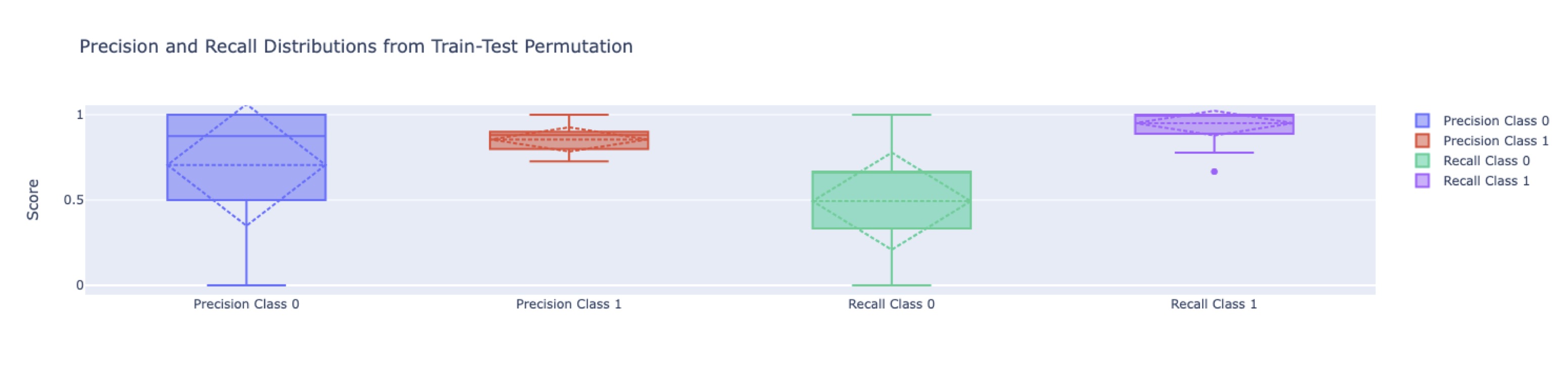 Figure 1 - Low model performance when using all feature. SVM model was used to evaluate Precision (True positive rate) and Recall (ability to classify all object of the target class) following Train/test permutation. Class 0 in old PRP and Class 1 is young PRP. Permutation of Train test groups allows to see the distribution of the Precision and Recall and is a good indicator of the quality of the ML model. We see that without features selection SVM model has poor performance predicting old PRP and achieved it with very high variability.
Figure 1 - Low model performance when using all feature. SVM model was used to evaluate Precision (True positive rate) and Recall (ability to classify all object of the target class) following Train/test permutation. Class 0 in old PRP and Class 1 is young PRP. Permutation of Train test groups allows to see the distribution of the Precision and Recall and is a good indicator of the quality of the ML model. We see that without features selection SVM model has poor performance predicting old PRP and achieved it with very high variability.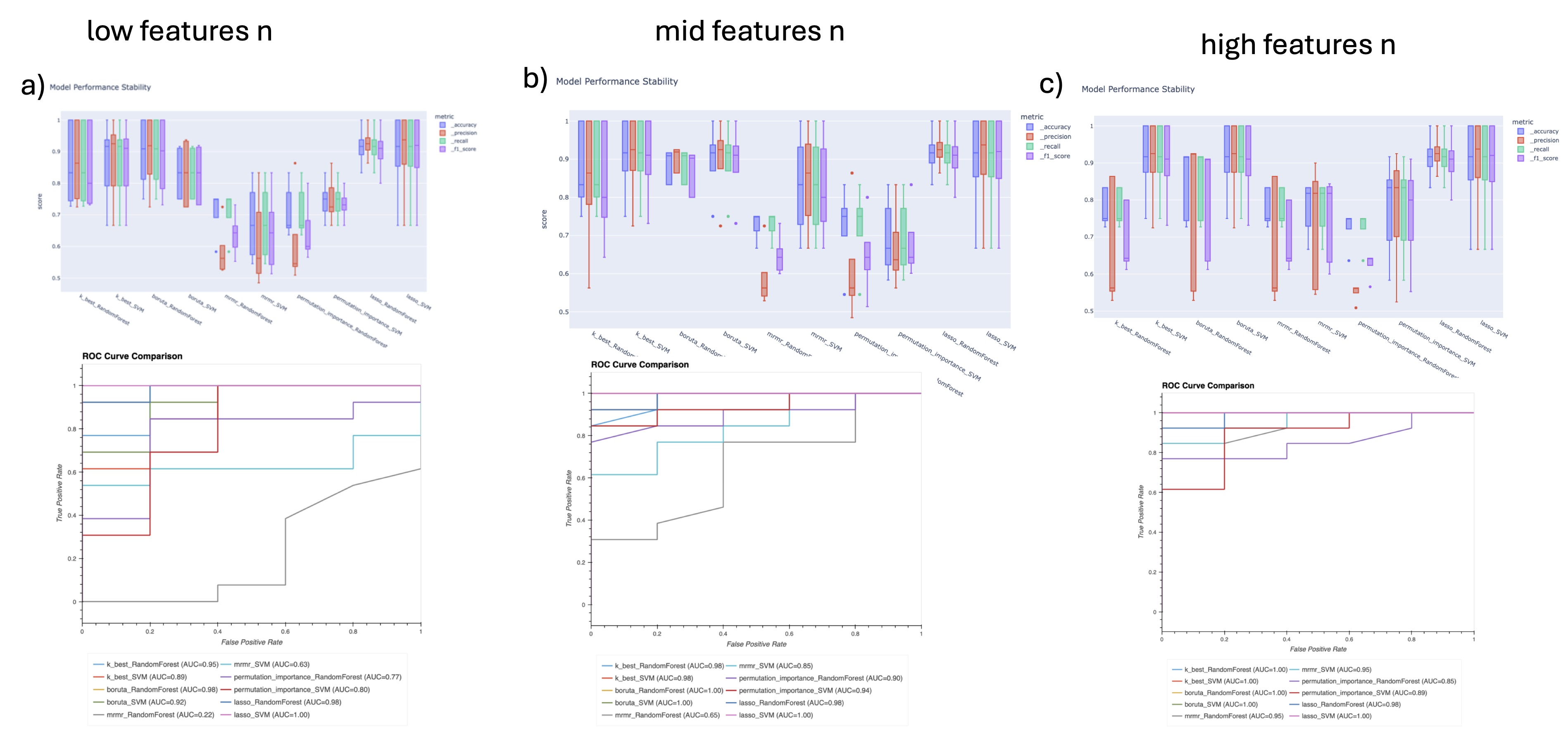 Figure 2 - Models metrics vs selections methods. 4 features selection method was tested to build machine learning based classifier (RF and SVM). Each method was tested a 3 different level of number of features (20 a), 100 b), 200 c)) when possible. Lasso doesn't allows to perform such selection, so it remains the same across test. Boruta doesn't allow to output a determined number of features put a stringency setting was used to output a similar number of features. Bottom pane present the ROC (receiver operating characteristic curve) for each pair and top present train/test permutation results on model precision, accuracy, recall and f1 score (a measure of predictive performance overall).
Figure 2 - Models metrics vs selections methods. 4 features selection method was tested to build machine learning based classifier (RF and SVM). Each method was tested a 3 different level of number of features (20 a), 100 b), 200 c)) when possible. Lasso doesn't allows to perform such selection, so it remains the same across test. Boruta doesn't allow to output a determined number of features put a stringency setting was used to output a similar number of features. Bottom pane present the ROC (receiver operating characteristic curve) for each pair and top present train/test permutation results on model precision, accuracy, recall and f1 score (a measure of predictive performance overall).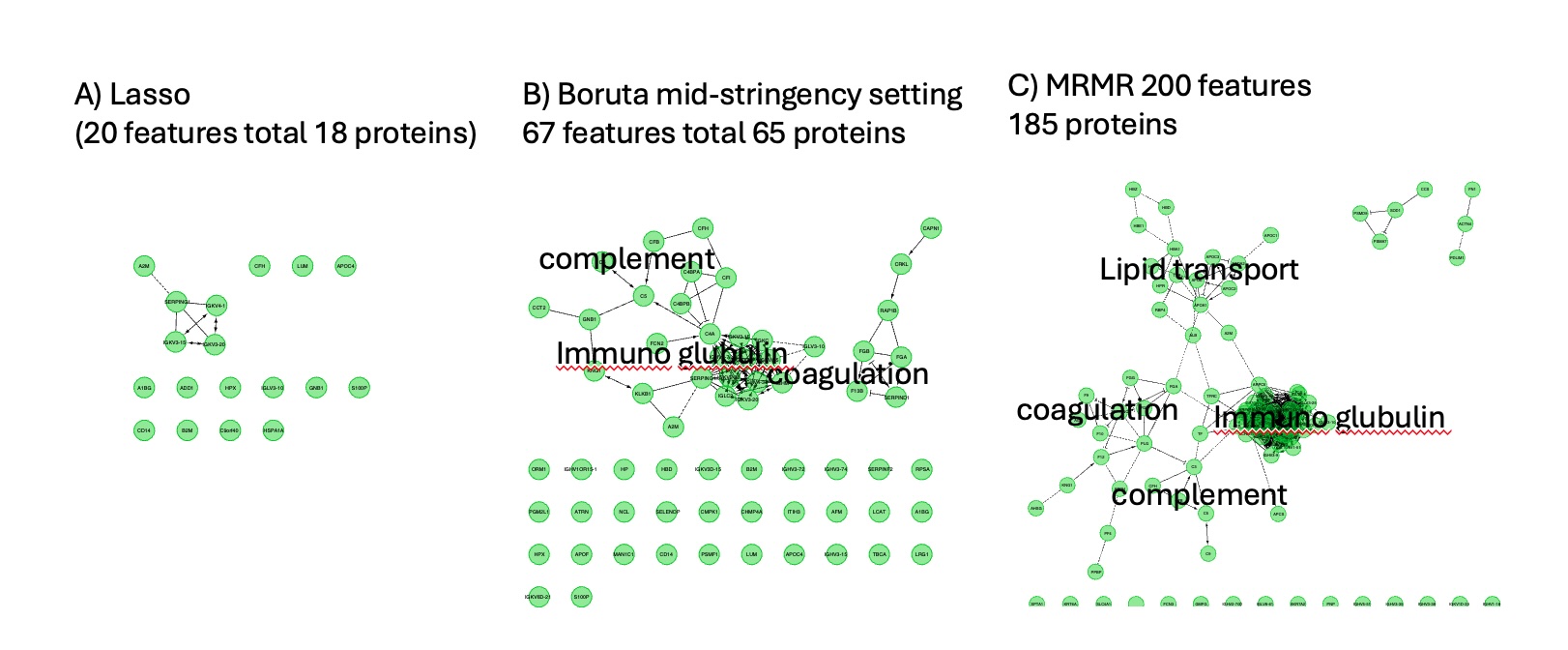 Figure 3 - Effect of features selection method on biological interpretability. Comparison of Reactom protein network of selected features. A) Lasso method, B) Boruta method with a percent setting at .9 and C) MRMR method with 200 selected features. Although MRMR method gave leaser performance in classification using RF and SVM, because more features were kept it's easier to interpret using GO and pathway analysis. We see key clusters of proteins having a define function. We see that B) still represent those key pathway ways in general but A) completely loses biological interpretability. However, A) still keep key proteins that are seen in C). This suggests we could perform features grouping prior to features selection to keep biological interpretability.
Figure 3 - Effect of features selection method on biological interpretability. Comparison of Reactom protein network of selected features. A) Lasso method, B) Boruta method with a percent setting at .9 and C) MRMR method with 200 selected features. Although MRMR method gave leaser performance in classification using RF and SVM, because more features were kept it's easier to interpret using GO and pathway analysis. We see key clusters of proteins having a define function. We see that B) still represent those key pathway ways in general but A) completely loses biological interpretability. However, A) still keep key proteins that are seen in C). This suggests we could perform features grouping prior to features selection to keep biological interpretability.