Formulation and Delivery - Chemical
(M1530-09-50) Exploring Manufacturing Techniques for Enhancing the Solubility of Fenbendazole: A Comparative Study of Hot-Melt Extrusion, Spray Drying, and KinetiSol® Processing
- MJ
Miguel O. Jara, Ph.D.
Research Fellow
University of Texas at Austin
Austin, Texas, United States - MJ
Miguel O. Jara, Ph.D.
Research Fellow
University of Texas at Austin
Austin, Texas, United States - GB
Giselle Bedogni, n/a
Graduate student
Universidad Nacional de Rosario
Rosario, Santa Fe, Argentina - LV
Lina Vargas Michelena, n/a
Graduate student
Universidad Nacional de Rosario
Rosario, Santa Fe, Argentina - DD
Daniel Davis, Ph.D.
Principal Scientist
AustinPx
Georgetown, Texas, United States - BB
Beatriz Behrend-Keim, n/a
Graduate Student
University of Texas at Austin
Austin, Texas, United States - DM
Dave Miller, Ph.D.
Chief Scientific Officer
AustinPx
Georgetown, Texas, United States - CS
Claudio Salomon, Ph.D.
Professor
Universidad Nacional de Rosario
Rosario, Santa Fe, Argentina 
Robert O. Williams, III, PhD (he/him/his)
Professor
The University of Texas at Austin
Austin, Texas, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Main Author(s)
Co-Author(s)
Methods: Thermogravimetric analysis (TGA): TGA was performed using a Mettler Thermogravimetric Analyzer, Model TGA/DSC 1 (Mettler Toledo, Columbus, OH). A physical mixture of Soluplus (SOL) and FBZ at a 1:1 ratio was evaluated (Figure 1A). Hot-melt extrusion: A FBZ/SOL blend (5/95 ratio) was processed using a HAAKE miniLab II Micro Compounder (Thermo Electron Corporation, Waltham, MA, USA) set at 100 rpm and 120°C. Spray drying: Initially, the solubility of crystalline FBZ was determined in several organic solvents such as Dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO), dimethylformamide (DMF), 1.4-dioxane, acetone, dichloromethane (DCM), ethyl acetate, methanol (MeOH), ethanol (EtOH), and acetonitrile (ACN), as well as 0.1 N HCl. An FBZ-SOL (5/95 ratio, 1 mg/mL of FBZ) solution in a DCM/MeOH (80/20) mixture was processed using a Mini Spray Dryer Buchi B-290 (Buchi Labortechnik AG, Switzerland). The inlet temperature was set at 70°C, and the feed rate was set at 5 mL/min. KinetiSol®: a FBZ/SOL blend (5/95 ratio) was mixed with magnesium stearate (0.5% of the mixture’s total weight). Then, the mixture was processed in the KinetiSol formulator, where it underwent mixing at 4000 RPM for 30 s, followed by processing at 6000 RPM with variable ejection temperatures. Sample characterization: WAXS was performed for 5 min using a SAXSLab instrument (WAXSLab, Northampton, MA, USA) to determine the solid state of the samples. On the other hand, LC–MS was employed to determine chemical degradation using an Agilent 6125B Single Quadrupole LC/MS coupled to an Agilent 1260 LC stack (Agilent Technologies Co., Santa Clara, CA). Dissolution test of crystalline FBZ, physical mixtures, and amorphous solid dispersions were performed in 0.1 N HCl using 200 mL vessels, 100 RPM paddle speed, and at 37 °C.
Results: TGA failed to predict the degradation temperature for HME compositions. Initially, thermal stability of the materials was assessed using TGA (Figure 1A). FBZ exhibited a mass loss at 158°C. Conversely, the FBZ-SOL physical mixture displayed mass losses at marginally lower temperatures (~150°C, excluding moisture). The blend was extruded at 120°C, as it was not extrudable at lower temperatures. The extrudate was amorphous, but LC-MS analysis revealed nearly complete degradation of FBZ (94% impurities). Fenbendazolamine was identified as the primary degradation product (Figure 1B). Spray drying is an option for preparing an ASD of FBZ, but design space is limited. Solvents suitable for dissolving FBZ were evaluated (Figure 2A). FBZ was more soluble in DMSO and DMF, but their high boiling points and low vapor pressures posed challenges for spray drying. Also, FBZ was soluble in 1.4-dioxane. However, upon testing this solvent, FBZ (299.3 g/mol) was oxidized into oxfendazole (315.3 g/mol), as confirmed by LC-MS. Ultimately, a 20% MeOH and 80% DCM mixture was utilized for spray drying a solution of FBZ at 0.1% (w/v). The final ASD was predominantly amorphous with minor crystallinity traces, as indicated by WAXS (Figure 2B). LC-MS analysis revealed no chemical degradation of the ASD; neither fenbendazolamine nor oxfendazole were detected. However, the manufacturing process was constrained by the low FBZ concentration in the cosolvent system. Literature suggests that spray drying typically necessitates a solids load between 5 and 50% (w/w), with higher solid loads yielding more cost-effective manufacturing (2). KinetiSol processing reduces the level of chemical degradation. The KinetiSol process was conducted at various ejection temperatures, as depicted in Figure 3A. A significant decrease in chemical degradation was observed at lower ejection temperatures, which resulted in a reduction of impurities in the processed materials. At the lowest ejection temperature, the sample exhibited ~6.4% impurities and was determined to be amorphous, according to WAXS (Figure 3B). This FBZ-KSD material enhanced the dissolution performance of FBZ (Figure 3C and 3D).
Conclusion: This study evaluated various manufacturing techniques for manufacturing an ASD of FBZ, a benzimidazole-carbamate anthelmintic with promising chemotherapeutic properties. While HME resulted in nearly complete degradation of FBZ, Spray Drying had limited utility due to the low FBZ concentration in the required cosolvent system. On the other hand, KinetiSol processing significantly reduced chemical degradation at lower ejection temperatures. These findings highlight the importance of selecting appropriate manufacturing techniques for formulating ASDs of thermally labile compounds like FBZ. Future research will focus on optimizing KinetiSol processing parameters to further reduce the impurities.
References: 1. Surasarang SH, Keen JM, Huang S, Zhang F, McGinity JW, III ROW. Hot melt extrusion versus spray drying: hot melt extrusion degrades albendazole. Drug Dev Ind Pharm [Internet]. 2017 May 4 [cited 2024 Jul 10]; Available from: https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/03639045.2016.1220577
2. Miller DA, Ellenberger D, Porfirio T, Gil M. Spray-Drying Technology. In: Williams III RO, Davis Jr. DA, Miller DA, editors. Formulating Poorly Water Soluble Drugs [Internet]. Cham: Springer International Publishing; 2022 [cited 2024 Jul 10]. p. 377–452. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-88719-3_10
Acknowledgements:
Funding: Miguel O. Jara and Beatriz Behrend-Keim were supported by AustinPx, Georgetown, TX, through a gift to support graduate education.
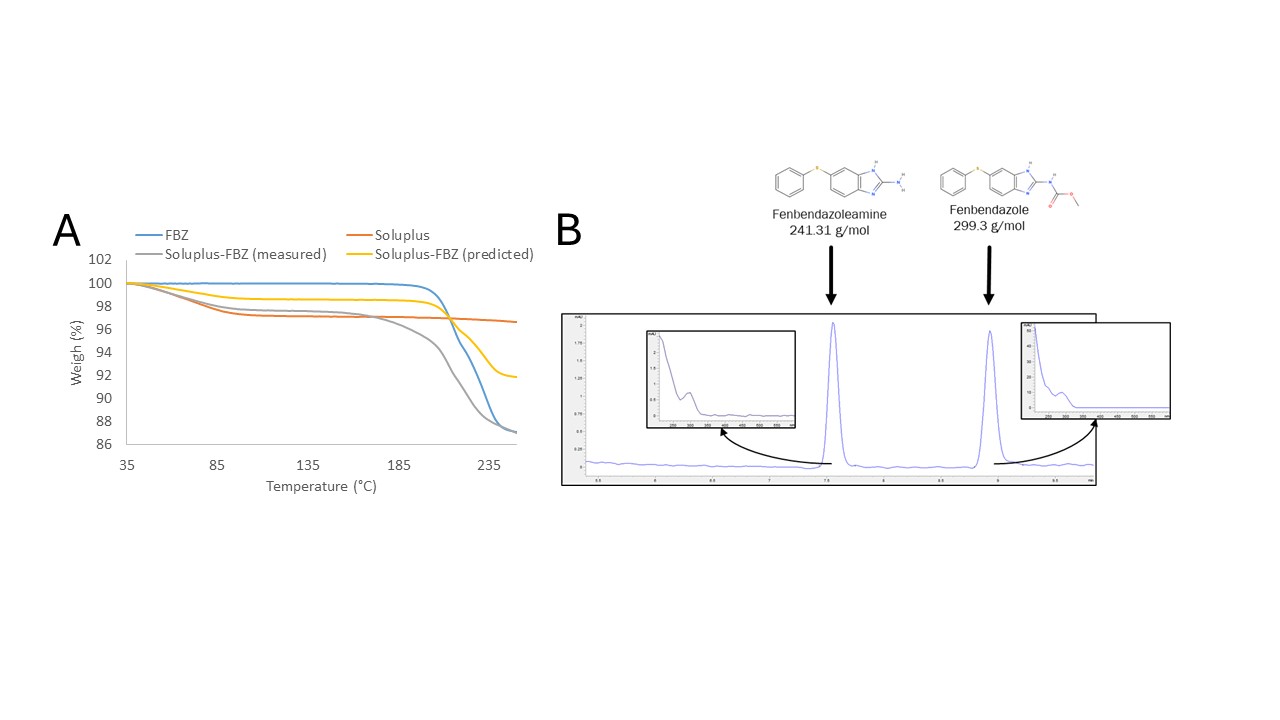 Figure 1. (A) TGA of FBZ, soluplus, and FBZ-soluplus physical mixture at 1:1 w/w ratio. (Additionally, the predicted weight loss of physical mixtures was added. It was considered the average of the FBZ and polymer curves). The samples were analyzed from 35°C to 250°C, using a heat rate of 10°C/min under Air 50 L/min. (B) Chromatogram of FBZ after undergoing thermal degradation
Figure 1. (A) TGA of FBZ, soluplus, and FBZ-soluplus physical mixture at 1:1 w/w ratio. (Additionally, the predicted weight loss of physical mixtures was added. It was considered the average of the FBZ and polymer curves). The samples were analyzed from 35°C to 250°C, using a heat rate of 10°C/min under Air 50 L/min. (B) Chromatogram of FBZ after undergoing thermal degradation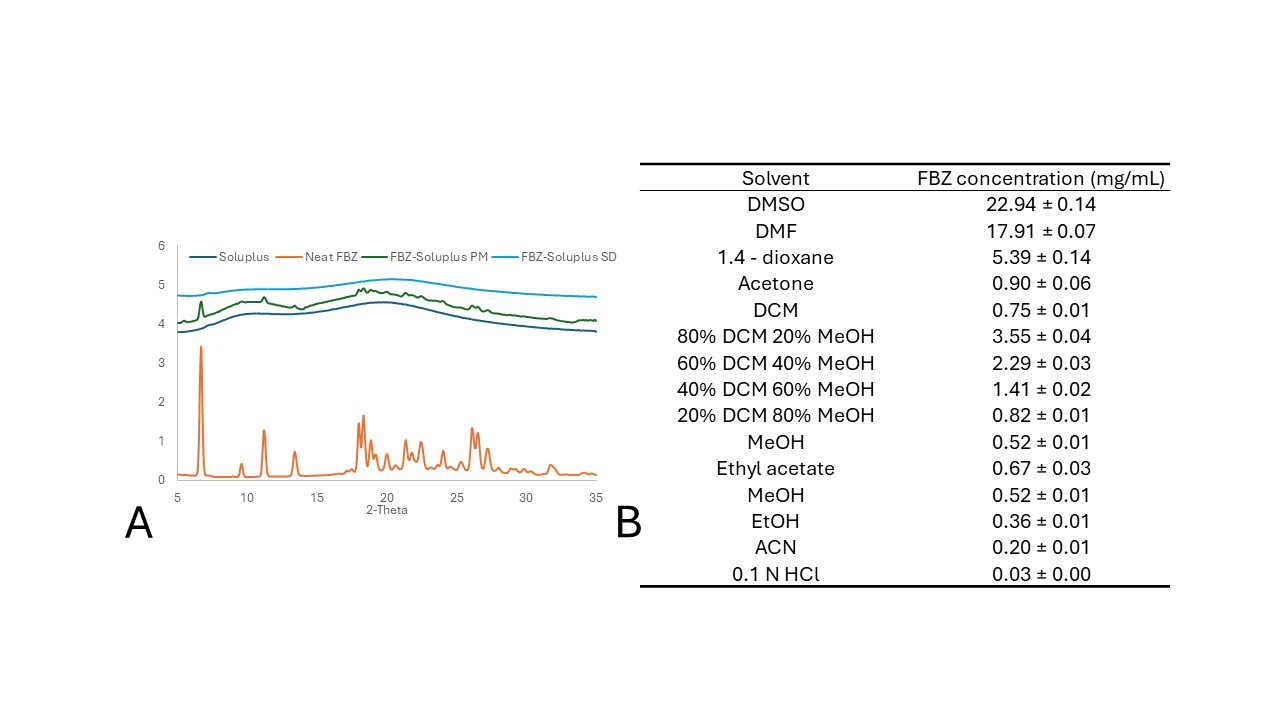 Figure 2. (A) Wide-angle X-ray diffractogram of crystalline FBZ, Soluplus, FBZ-Soluplus physical mixture, and FBZ-SD. (B) Solubility of FBZ in different solvent and cosolvent systems.
Figure 2. (A) Wide-angle X-ray diffractogram of crystalline FBZ, Soluplus, FBZ-Soluplus physical mixture, and FBZ-SD. (B) Solubility of FBZ in different solvent and cosolvent systems. 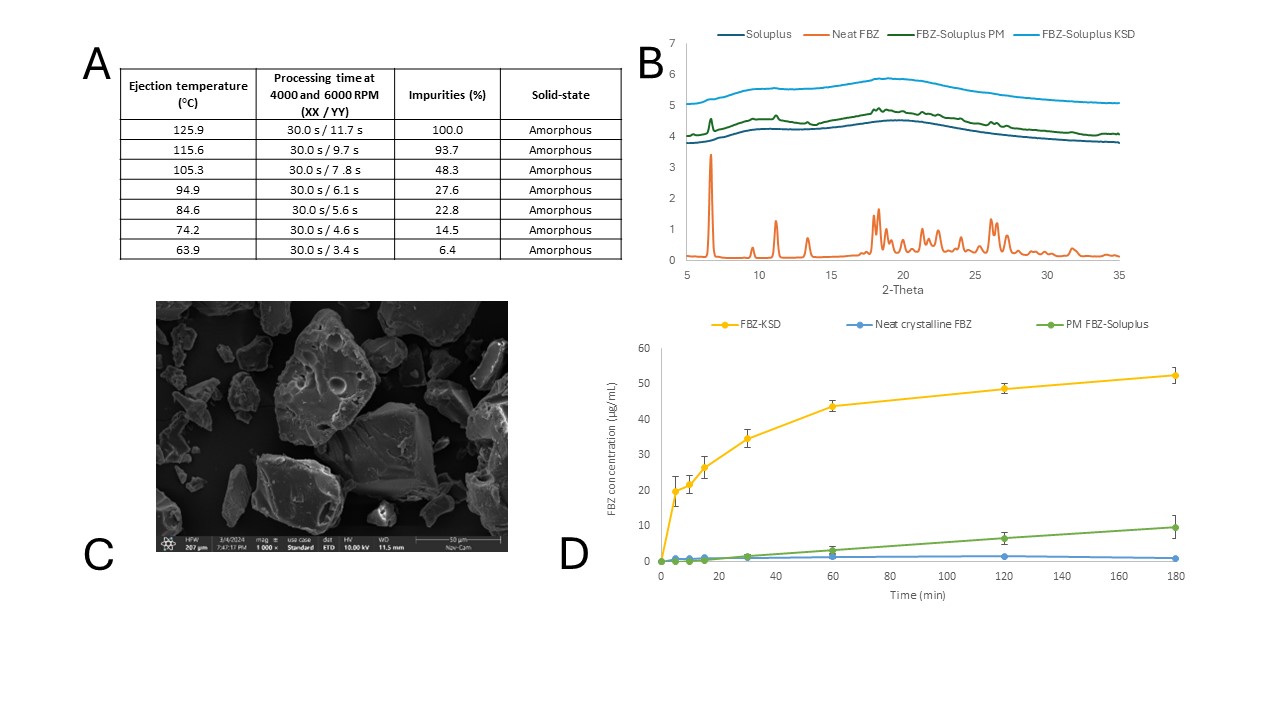 Figure 3. (A) FBZ potencies and solid-state after KinetiSol processing at different ejection temperatures. The samples were analyzed using LC-MS and WAXS. The sample with the lowest level of impurities was employed for further testing (FBZ-KSD). (B) Wide-angle X-ray diffractogram of crystalline FBZ, Soluplus, FBZ-Soluplus physical mixture, and FBZ-KSD. (C) SEM picture of FBZ-KSD . The bar shows a size of 50 µm. (D) Dissolution profile of neat crystalline FBZ, physical mixture of FBZ-Soluplus, and FBZ-KSD.
Figure 3. (A) FBZ potencies and solid-state after KinetiSol processing at different ejection temperatures. The samples were analyzed using LC-MS and WAXS. The sample with the lowest level of impurities was employed for further testing (FBZ-KSD). (B) Wide-angle X-ray diffractogram of crystalline FBZ, Soluplus, FBZ-Soluplus physical mixture, and FBZ-KSD. (C) SEM picture of FBZ-KSD . The bar shows a size of 50 µm. (D) Dissolution profile of neat crystalline FBZ, physical mixture of FBZ-Soluplus, and FBZ-KSD.