Formulation and Delivery - Biomolecular
(T0930-09-48) Cationic CaMKIIN-Loaded Liposomes that Reduce Chlorine-Induced Airway Oxidative Stress

Esraa Mohamed, MS (she/her/hers)
PhD Graduate candidate
University of Iowa
Iowa City, Iowa, United States
Esraa Mohamed, MS (she/her/hers)
PhD Graduate candidate
University of Iowa
Iowa City, Iowa, United States- AA
Andrea Adamcakova-Dodd, Ph.D.
Asst Research Scientist
University of Iowa
Iowa City, Iowa, United States - IG
Isabella Grumbach, Ph.D.
Departmental Executive Officer
University of Iowa
Iowa City, Iowa, United States - PT
Peter Thorne, Ph.D.
Professor, Occupational & Environmental Health department
University of Iowa
Iowa City, Iowa, United States - XJ
Xuefang Jing, Ph.D.
Research Assistant, Occupational & Environmental Health department
University of Iowa
Iowa City, Iowa, United States 
Aliasger K. Salem, Ph.D.
Associate Vice President for Research
University of Iowa
Iowa City, Iowa, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Main Author(s)
Co-Author(s)
Methods: Firstly, a pilot study was conducted by exposing C57BI6/J female mice to two concentrations of chlorine: 200ppm and 250ppm for 20 mins. Then 4h or 24h following the exposure, pulmonary mechanics were assessed using airway hyper-reactivity test (methacholine challenge). In addition, total protein levels, IL-6 levels, TNF-α and total and differential cell counts in the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) following the chlorine exposure were assessed to confirm inflammation and injury occurring in the lung tissues after the exposure. Furthermore, the levels of oxidized CaMKII in the lung tissues following chlorine exposure were evaluated using immunofluorescence staining. To explore the hypothesis that inhibition of CaMKII activity can mitigate chlorine-induced lung injury in vivo, CaMKII inhibitor peptide (CaMKIIN) was loaded into liposomes (LPs) using a microfluidics technique. After that, C57BI6/J female mice (n= 6 per group) were exposed to 200ppm chlorine gas for 20 mins, and immediately after the exposure, mice received either phosphate buffered saline (PBS) or treatment by oropharyngeal aspiration (OA). The assigned treatments were LPs equivalent to either 25 ng or 150 ng CaMKIIN or 25 ng CaMKIIN solution in PBS. The total protein levels, total and differential cell counts were evaluated 24 h after treatment.
Results: There was a dose-dependent increase in pulmonary responsiveness to methacholine reflected in all the parameters of lung function. Chlorine gas induced significant airway hyperresponsiveness following methacholine challenge in both dose groups 24 h post-exposure. Similarly, there was a significant dose-dependent increase in the BALF protein levels, and cell counts. 24 h following chlorine exposure confirming that inflammation and injury occurred in the lung epithelium. In addition, there was a significant increase in IL-6 and TNF-α levels in the BALF of the mice group exposed to 250ppm chlorine and euthanized 4h after exposure. Notably, the oxidation of CaMKII in the lung tissues significantly increased after chlorine exposure in the group exposed to 250 ppm and the activation was the highest 4 h after exposure. These results support our hypothesis that chlorine exposure triggers the activation of CaMKII through oxidation and CaMKII is one of the targets that shortly activated after chlorine exposure. The prepared CaMKIIN-loaded LPs had a uniform size distribution (63.7 ± 7.5 nm diameter with PDI = 0.13± 0.07) with a positive charge (6.33 ± 0.36 mV) and showed minimal cytotoxicity. After LP administration to mice exposed to chlorine, there was a decrease in total protein levels, and total cell counts of the group treated with CaMKIIN-loaded LPs, however, the difference between treatment groups was non-significant. We are currently optimizing our dosage regimen for CaMKIIN-loaded LPs and also exploring the efficacy of other CaMKII inhibitors.
Conclusion: In conclusion, this study proved that airway hyperreactivity and lung injury occurred following chlorine exposure. Also confirmed was the significant increase in oxidized CaMKII levels in response to chlorine inhalation. However, the administered treatment was insufficient to significantly prevent chlorine induced injury. Dose screening will be explored in future treatment studies. In addition, different CaMKII inhibitors will be considered in upcoming animal studies.
Acknowledgements: This work is funded by the NIH CounterACT R21 Grant-R21ES032937.
.jpg) Figure 1: Pulmonary resistance (A), differential cell counts (B) of in the BALF of animal groups unexposed and exposed to different chlorine gas concentrations (values represent means ± SD). Statistical analysis was performed using one-way ANOVA, followed by Tukey’s post-hoc test. P-values of less than or equal to 0.05 were considered significant., *p <0.05, ** p <0.01, ***p <0.001, ****p <0.0001.
Figure 1: Pulmonary resistance (A), differential cell counts (B) of in the BALF of animal groups unexposed and exposed to different chlorine gas concentrations (values represent means ± SD). Statistical analysis was performed using one-way ANOVA, followed by Tukey’s post-hoc test. P-values of less than or equal to 0.05 were considered significant., *p <0.05, ** p <0.01, ***p <0.001, ****p <0.0001.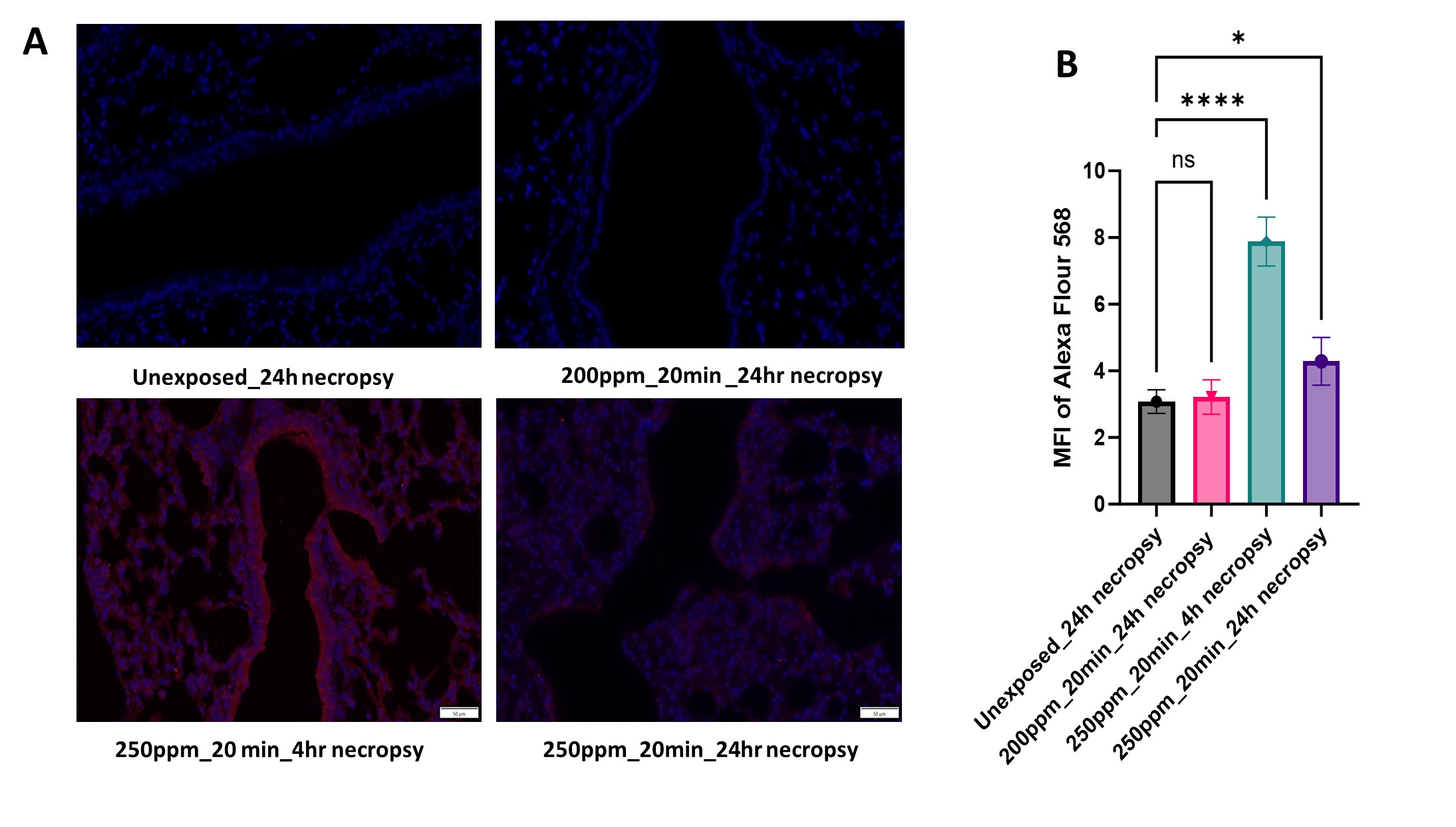 Figure 2: Fluorescence microscope images of lung tissues (A) and the mean fluorescence intensity measured by image J (B) of oxidized CaMKII levels in lung tissues unexposed and exposed to 200 ppm or 250 ppm chlorine concentration for 20 min measured by Alexa Flour 568 (values represent means ± SD). Statistical analysis was performed using one-way ANOVA, followed by Tukey’s post-hoc test. P-values of less than or equal to 0.05 were considered significant, *p <0.05, ** p <0.01, ***p <0.001, ****p <0.0001.
Figure 2: Fluorescence microscope images of lung tissues (A) and the mean fluorescence intensity measured by image J (B) of oxidized CaMKII levels in lung tissues unexposed and exposed to 200 ppm or 250 ppm chlorine concentration for 20 min measured by Alexa Flour 568 (values represent means ± SD). Statistical analysis was performed using one-way ANOVA, followed by Tukey’s post-hoc test. P-values of less than or equal to 0.05 were considered significant, *p <0.05, ** p <0.01, ***p <0.001, ****p <0.0001.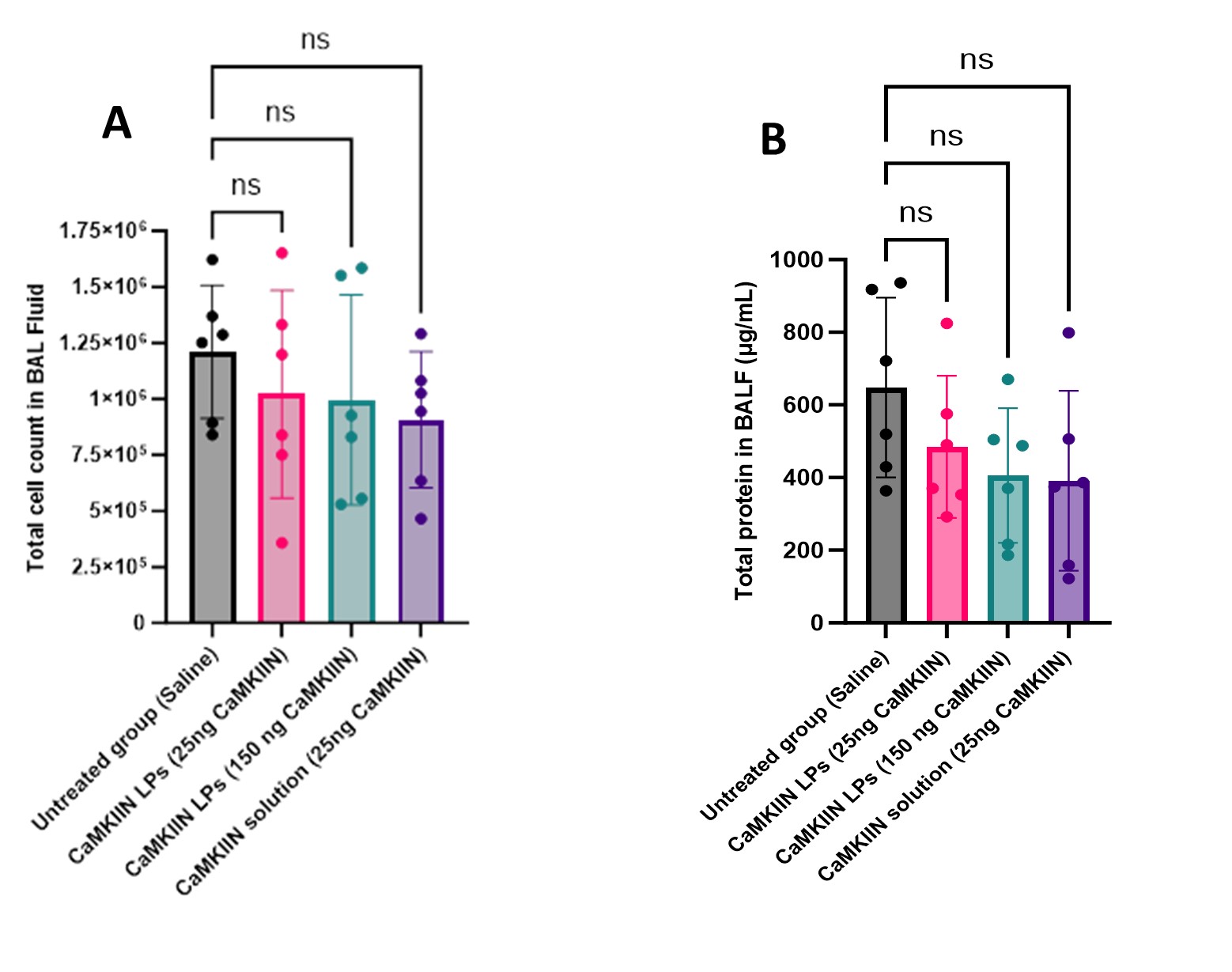 Figure 3: Total cell counts (A), and total protein concentrations measured using microBCA (B) in the BALF of exposed mice to 200 ppm for 20 min and receiving either saline or CaMKIIN treatment (values represent means ± SD). Statistical analysis was done using one-way ANOVA, followed by Tukey’s post-hoc test. P-values of less than or equal to 0.05 were considered significant.
Figure 3: Total cell counts (A), and total protein concentrations measured using microBCA (B) in the BALF of exposed mice to 200 ppm for 20 min and receiving either saline or CaMKIIN treatment (values represent means ± SD). Statistical analysis was done using one-way ANOVA, followed by Tukey’s post-hoc test. P-values of less than or equal to 0.05 were considered significant.