Formulation and Delivery - Chemical
(T1130-09-48) Rapid Production of Personalized Breast Cancer Medicines for Inclusion in a Clinical Trial Using a Novel Pharmaceutical 3D Printing Platform in a Hospital
- XR
Xela Rodriguez Maciñeiras, MS
Researcher
FABRX Ltd
Santiago de Compostela, Galicia, Spain - LD
Lucas Denis, MS
Pharmacist
Gustave Roussy Cancer Campus
Paris, Ile-de-France, France 
Anna Kirstine Jorgensen, MS (she/her/hers)
PhD student
University College London
London, England, United Kingdom- BD
Bernard Do, Pharm.D.
Pharmacist
Gustave Roussy Cancer Campus
Paris, Ile-de-France, France - IV
Inès Vaz-Luis, Pharm.D.
Pharmacist
Gustave Roussy Cancer Campus
Paris, Ile-de-France, France - BP
Barbara Pistilli, Pharm.D.
Pharmacist
Gustave Roussy Cancer Campus
Paris, Ile-de-France, France - AR
André Rieutord, Pharm.D.
Pharmacist
Gustave Roussy Cancer Campus
Paris, Ile-de-France, France - AB
Abdul W. Basit, Pharm.D.
Researcher
University College London
London, England, United Kingdom 
Álvaro Goyanes, Pharm.D.
Researcher
FabRx Ltd
Kent, England, United Kingdom- MA
Maxime Annereau, Pharm.D.
Pharmacist
Gustave Roussy Cancer Campus
Paris, Ile-de-France, France
Presenting Author(s)
Main Author(s)
Co-Author(s)
Methods: Formulation preparation. A pharma-ink containing tamoxifen citrate (TC) (30% w/w) was prepared by melting polyethylene glycol (PEG) 4000 at 75 °C before dispersion of TC under mechanical stirring at 800 rpm for one hour. The pharma-ink was immediately transferred to 20 ml sterile, Luer lock syringes and capped. For venlafaxine, duloxetine, and placebo, commercial controlled release pellets were used. Capsule filling. The M3DIMAKER2 pharmaceutical 3D printer was utilised to first fill each of 200 size 1 gelatine capsules with 101.1 mg TC pharma-ink through the semisolid extrusion printhead before the subsequent dispensing of venlafaxine, duloxetine, or placebo pellets using a newly developed pellet dispensing printhead accessory from FABRX. Characterization of developed medicines. Mass uniformity assessments were carried out for both TC pharma-ink deposition and pellet dispensing methods. The solid state of TC in the pharma-ink was determined using differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) and X-ray powder diffraction (XRPD). TC loading and in vitro drug release for tamoxifen, venlafaxine, and duloxetine were performed and compared to commercial dosage forms according to their USP monographs with samples withdrawn at specified timepoints and analysed through HPLC by validated methods for each of the actives. Stability test. All combinations of actives and doses were subjected to a stability study by placing the medicines in PVC-PVDC blister packages stored in humidity chambers set at 25 °C, 50% relative humidity (RH) and 40 °C, 75% RH. Dissolution profiles of each active from the medicine was investigated after 3 months of storage an analysed via HPLC, with identification of any degradation products as identified through forced API degradation studies. A thermal stress study was conducted on TC by placing it in an oven at 100 °C for seven days, with TC content analysis via HPLC on days 0, 2, 4, and 7.
Results: Size 1 capsules were successfully filled with both tamoxifen pharma-ink and venlafaxine, duloxetine, or placebo pellets, an overall reduction in medication burden compared to commercially available dosage forms (figure 1). The optimal extrusion value for depositing TC pharma-ink was found to be 2.8, resulting in an average fill mass of 107 ± 4.35 mg, conforming the European Pharmacopeia acceptance value for uniformity of mass of oral solid dosage forms. Precise pellet dispensing was obtained with a relative standard deviation (RSD) of 1.09%. The novel capsule filling approach enabled the complete filling of a capsule in less than 10 seconds and an overall production of 200 dose units with a mean time of only 45 minutes, including time for pharma-ink preparation, printer initiation, capsule filling, and analytical assessments. XRPD and DSC analyses revealed that TC was still present in its crystalline form but that partial TC solubilisation during heat processing might occur (figure 2). A delay in initial in vitro tamoxifen release from the developed medicines was observed compared to the commercial tablets, which was likely the result of the lag-time for capsule shell disintegration. Nonetheless, release specifications of not less than 75% release tamoxifen were met for medicines immediately after production as well as post stability testing at ambient and accelerated conditions (figure 3). Venlafaxine and duloxetine release also conformed to USP specifications and remained unaltered during the stability test. No degradation products were observed during the stability test for the developed medicines not for TC during the thermal stress study.
Conclusion: A novel and rapid capsule filling platform was implemented in a hospital pharmacy for the development and production of personalised tamoxifen medicines in combination with either venlafaxine or duloxetine in one of two doses or a placebo for the purpose of a large clinical trial. The quality of the medicines was demonstrated according to pharmacopeial requirements, and all obtained data was submitted to the French regulatory body.
References: 1. de Souza, J.A. and O.I. Olopade, CYP2D6 genotyping and tamoxifen: an unfinished story in the quest for personalized medicine. Semin Oncol, 2011. 38(2): p. 263-73.
2. Trayes, K.P. and S.E.H. Cokenakes, Breast Cancer Treatment. Am Fam Physician, 2021. 104(2): p. 171-178.
3. Mao, D., et al., Treatment interruption and discontinuation of hormonal therapy in hormone receptor-positive breast cancer patients. Breast Cancer Res Treat, 2020. 184(3): p. 665-674.
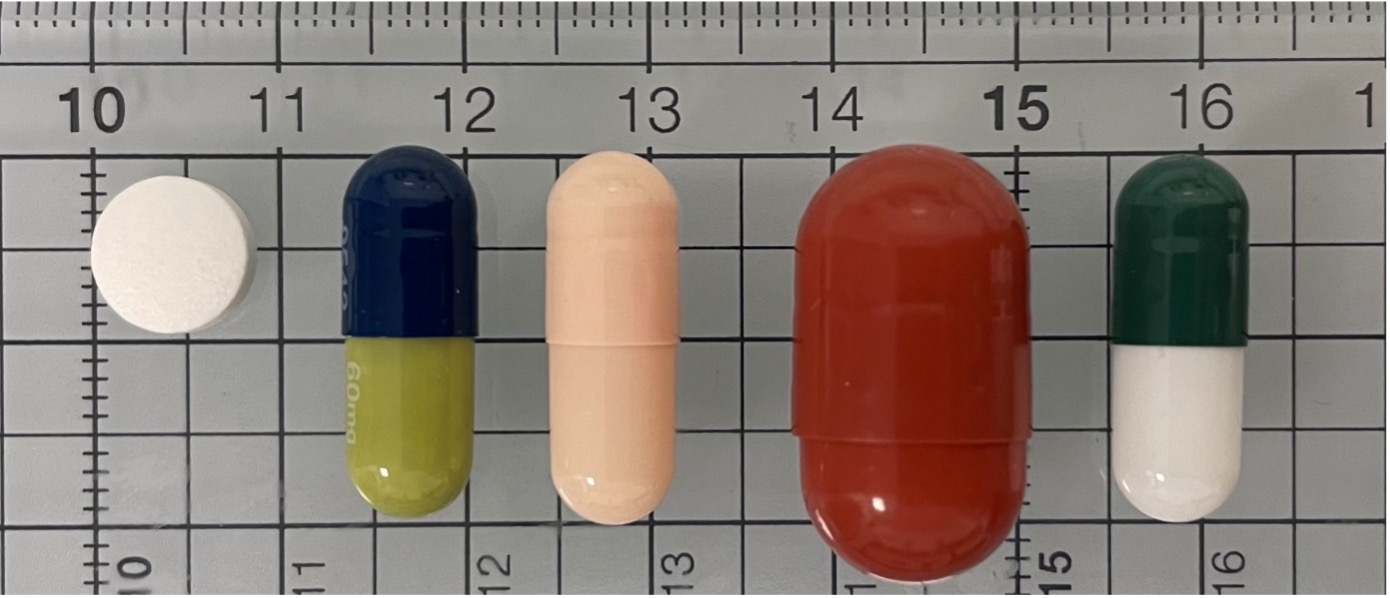 Figure 1. Image depicting (from left to right) commercial tamoxifen tablet, commercial duloxetine and venlafaxine capsules, commercial masking capsule, and developed medicine in the hospital using a pharmaceutical 3D printer. Scale in cm.
Figure 1. Image depicting (from left to right) commercial tamoxifen tablet, commercial duloxetine and venlafaxine capsules, commercial masking capsule, and developed medicine in the hospital using a pharmaceutical 3D printer. Scale in cm.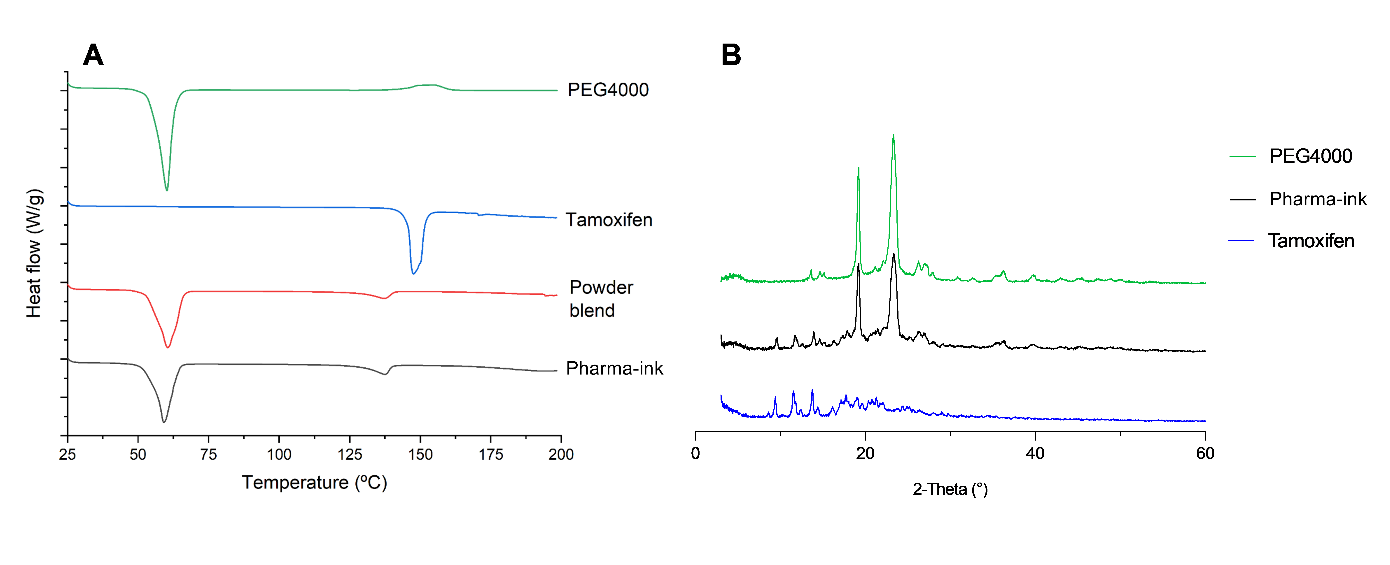 Figure 2. XRPD diffractograms and DSC thermograms of raw materials (tamoxifen citrate and PEG 4000) as well as powder blend and pharma-ink
Figure 2. XRPD diffractograms and DSC thermograms of raw materials (tamoxifen citrate and PEG 4000) as well as powder blend and pharma-ink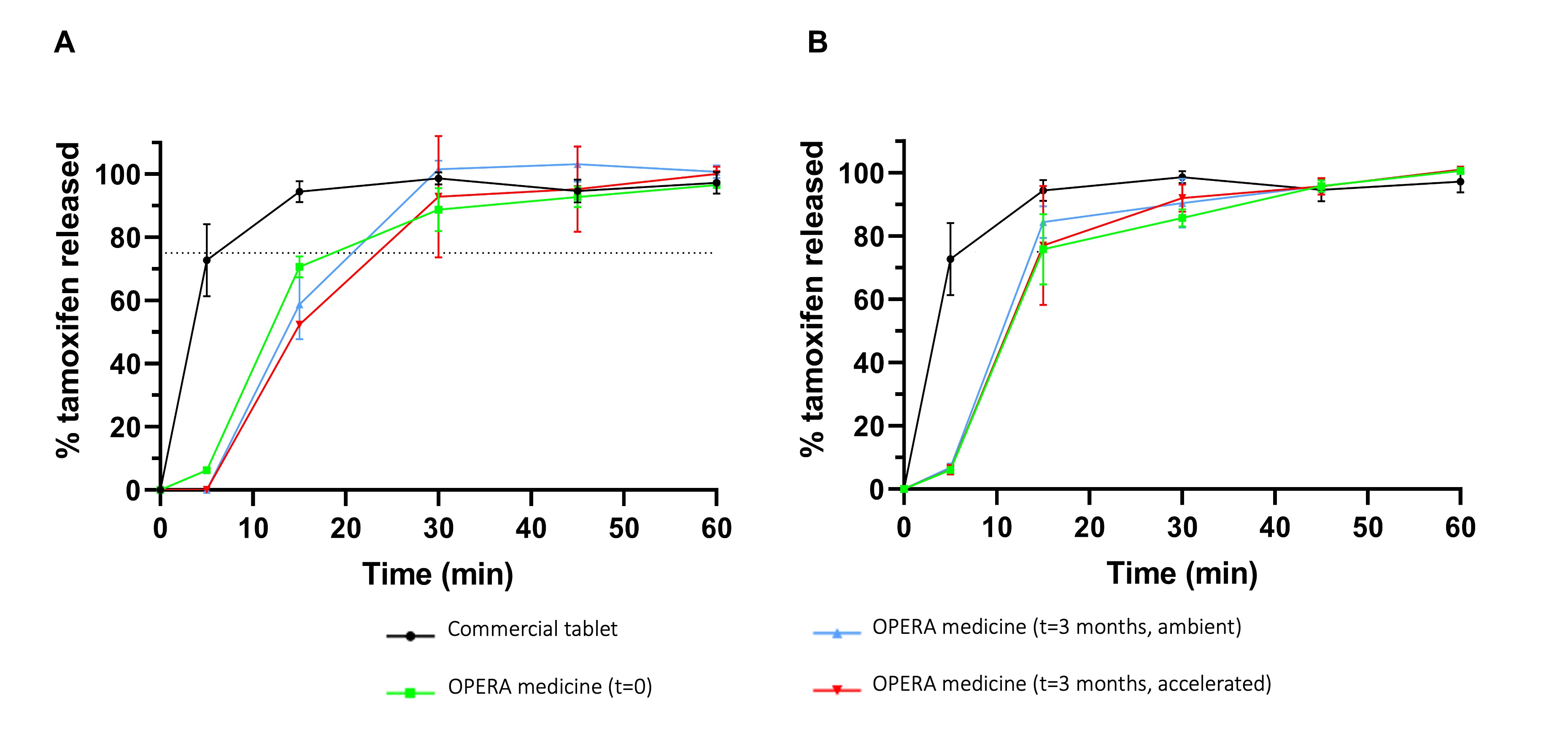 Figure 3. Dissolution profiles of tamoxifen from commercial tablets (black) compared to the developed medicines at t=0 (green) as well as t=3 months at ambient conditions (blue) and t=3 months at accelerated conditions (red) for medicines also containing A) duloxetine and B) venlafaxine.
Figure 3. Dissolution profiles of tamoxifen from commercial tablets (black) compared to the developed medicines at t=0 (green) as well as t=3 months at ambient conditions (blue) and t=3 months at accelerated conditions (red) for medicines also containing A) duloxetine and B) venlafaxine.