Formulation and Delivery - Chemical
(T1330-07-39) Hot Melt Extruded Amorphous Solid Dispersions Containing Lumefantrine and Soluplus
Tuesday, October 22, 2024
1:30 PM - 2:30 PM MT
- MG
Mael Gallas, Pharm.D.
Manager Business Development North America and France, PhD Candidate
Rondol Industrie
Nancy, Lorraine, France - SL
Shu Li, Ph.D.
Senior Lecturer
Queen's University Belfast
Belfast, Northern Ireland, United Kingdom 
Victoire de Margerie, Ph.D.
Executive Chairman
Rondol Industrie
NANCY, Lorraine, France- PB
Pascal Boulet, Ph.D.
Chief of Department CC X Gamma
Institut Jean Lamour
NANCY, Lorraine, France 
Gavin P. Andrews, Ph.D. (he/him/his)
Chair of pharmaceutical engineering
Queen's University Belfast
Belfast, Northern Ireland, United Kingdom
Presenting Author(s)
Main Author(s)
Co-Author(s)
Purpose: To address the poor solubility of lumefantrine (LUM) in gastrointestinal fluids while using hot melt extrusion (HME) to create amorphous solid dispersions (ASDs) of LUM within Soluplus® based matrices as a first step to develop more efficient and lower cost treatment of child malaria.
Methods: Amorphous solid dispersions of lumefantrine with Soluplus® were prepared using hot melt extrusion. Various processing parameters, including temperature profiles and production scales, were evaluated to optimize the drug loading and physical stability. Techniques like DSC, PXRD, and in-vitro dissolution testing were employed to characterize the formulations and assess their performance.
Results: ASDs were successfully produced with different drug loadings (30% and 50% w/w LUM) and extrusion conditions. Higher processing temperatures and vertical scaled-up production improved amorphization and dissolution rates. F1 formulations with 30% w/w LUM showed superior dissolution compared to F2 with 50% w/w. Stability studies indicated some recrystallization over six months, but formulations still exhibited much better performance than commercial Riamet® tablets.
Conclusion: Vertical HME effectively improved the solubility and dissolution of LUM in Soluplus® matrices. High drug loading was achieved, but maintaining physical stability remains a challenge. The study highlights the potential of Vertical HME in developing effective anti-malarial formulations with enhanced bioavailability.
References: 1. Alhalaweh et al., 2014, Mol Pharm
2. AL-Japairai et al., 2023, Int J Pharm
3. Amin et al., 2013, Malar J
4. Armstrong et al., 2023, J Pharm Sci
5. Badman et al., 2019, J Pharm Sci
6. Bhattacharyya & Ramachandran, 2022, Materials Letters: X
7. Bhujbal et al., 2021, J Pharm Sci
8. Civati et al., 2021, Cryst Growth Des
9. de Freitas-Marques et al., 2020, J Struct Chem
10. de Margerie et al., 2021, Int J Pharm
11. Djimdé & Lefèvre, 2009, Malar J
12. Donnelly et al., 2015, Pharm Res
13. Hassan Shah et al., 2021, J Drug Deliv Sci Technol
14. Jain et al., 2017
15. Karunanithy & Muthukumarappan, 2011, Biosyst Eng
16. Kelleher et al., 2018, Int J Pharm
17. Li et al., 2016, AAPS PharmSciTech
18. Medicines for Malaria Venture, 2015
19. Meng et al., 2010, Food Research International
20. Ogutu et al., 2023, Lancet Infect Dis
21. Pawar & Shende, 2020, Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp
22. Shantanu et al., 2006, PCT/IB2006/001037
23. Su et al., 2009, International Journal of Food Engineering
24. Tian et al., 2013, Mol Pharm
25. Trasi et al., 2020, Int J Pharm X
26. Volpe-Zanutto et al., 2021, Journal of Controlled Release
27. Wahajuddin et al., 2011, Malar J
28. Weuts et al., 2003, Int J Pharm
29. World Health Organization, 2022
30. Yao et al., 2021, J Pharm Sci
31. Yenet et al., 2023, ClinicoEconomics and Outcomes Research
32. Zhou et al., 2002, J Pharm Sci
Acknowledgements: This work was supported by the following entities: The School of Pharmacy, Queen’s University Belfast; Institut Jean Lamour, Nancy, France; Rondol Industrie, Nancy, France
We acknowledge the assistance of Kemprotec Limited for providing lumefantrine and BASF Corporation for supplying Soluplus®.
No conflicts of interest were declared by the authors.
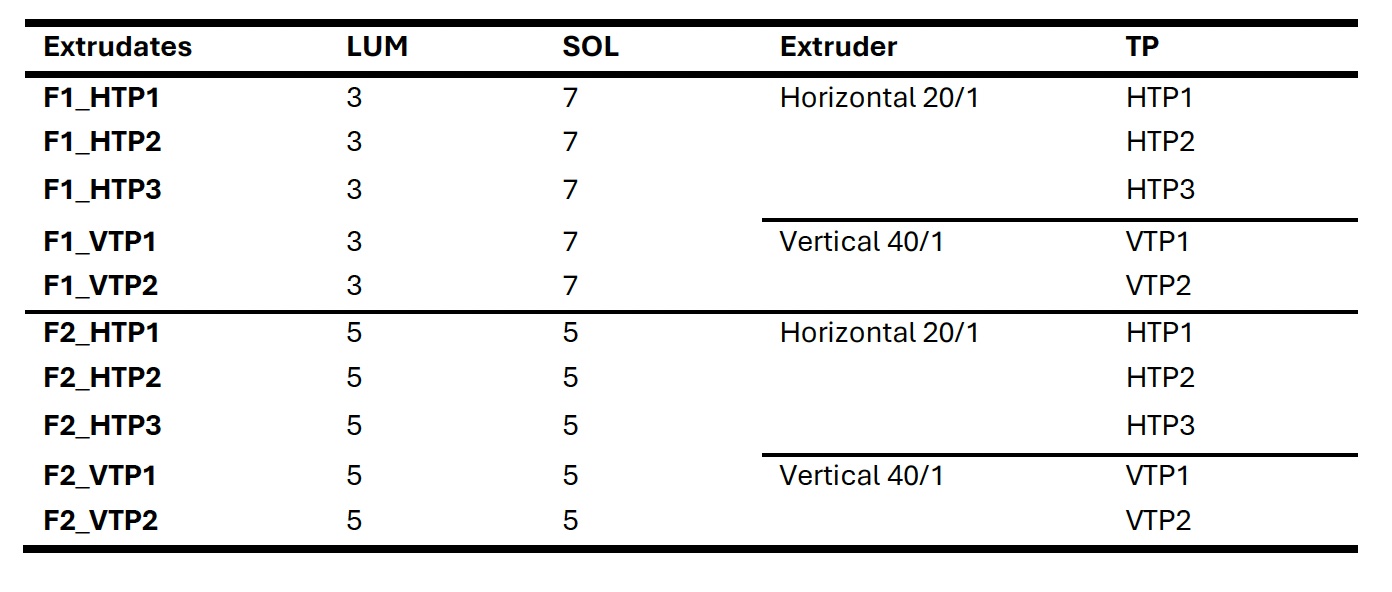 Table 1: Nomeclature of the formulations extruded in this study.
Table 1: Nomeclature of the formulations extruded in this study.
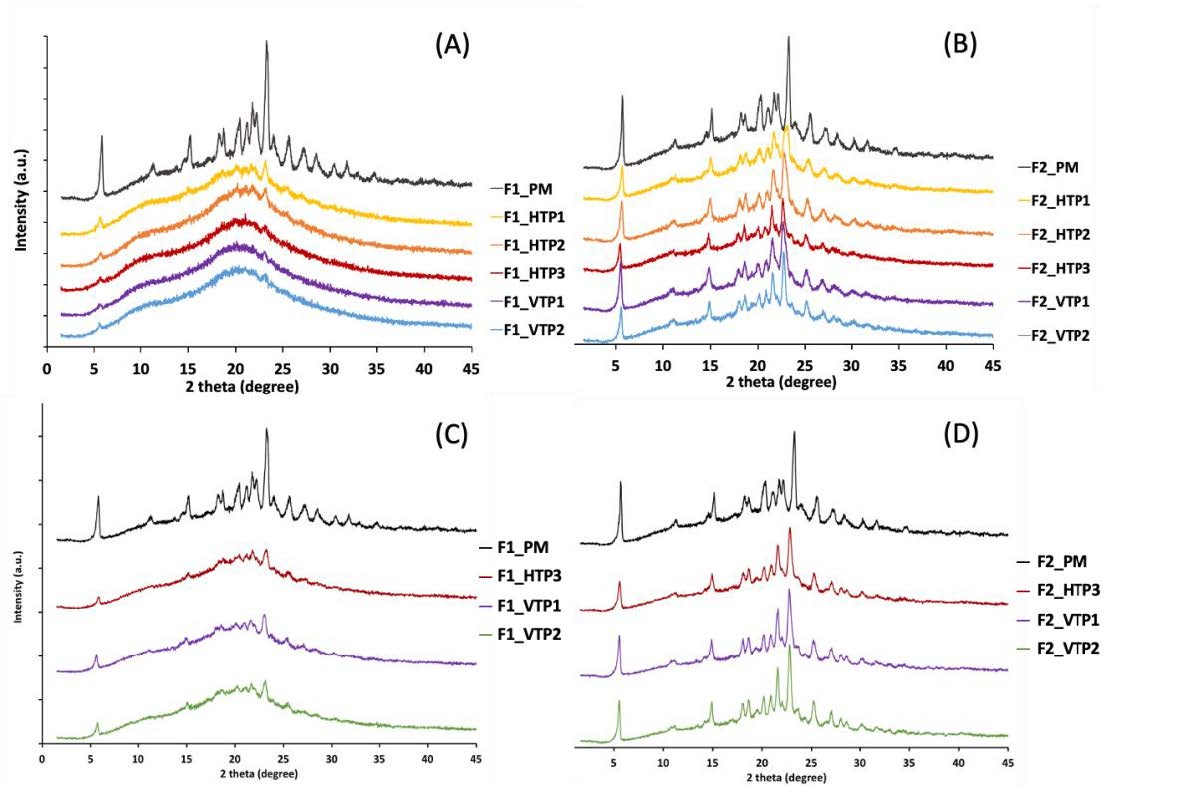 Figure 1. PXRD patterns of extruded formulations following storage under accelerated conditions (A) F1 extrudates over a 2-week period; (B) F2 extrudates over a 2-week period; (C) F1 extrudates over a 6-month period; and (D) F2 extrudates over a 6-month period. Note that the PXRD pattern of the physical mixture of each formulation is presented at the top of each diffractogram for comparison.
Figure 1. PXRD patterns of extruded formulations following storage under accelerated conditions (A) F1 extrudates over a 2-week period; (B) F2 extrudates over a 2-week period; (C) F1 extrudates over a 6-month period; and (D) F2 extrudates over a 6-month period. Note that the PXRD pattern of the physical mixture of each formulation is presented at the top of each diffractogram for comparison.
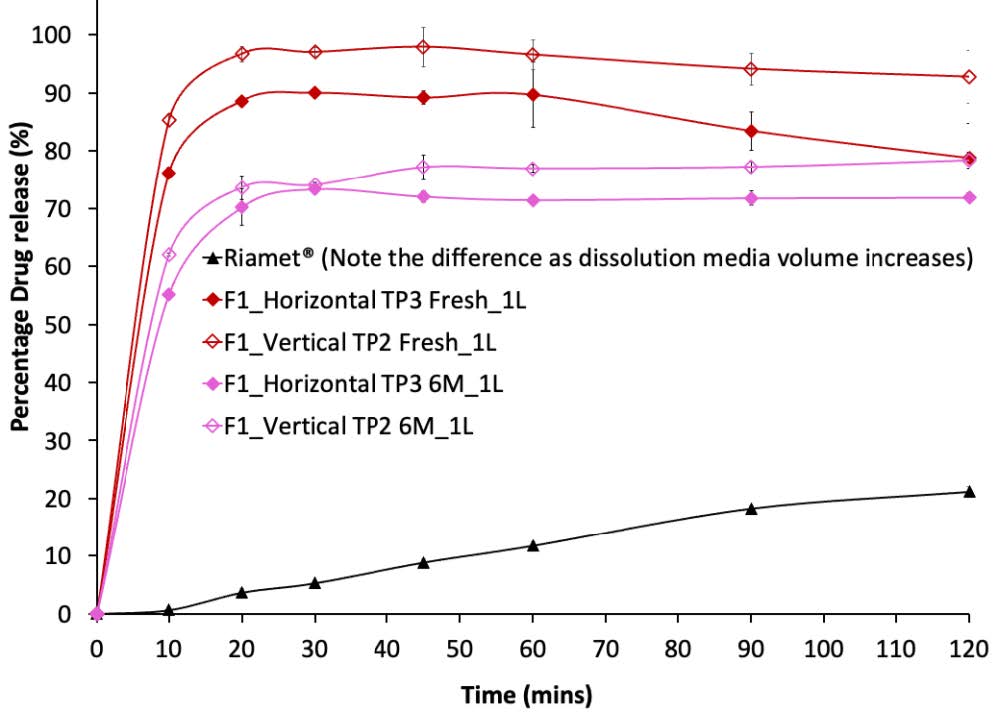 Figure 2. In-vitro drug dissolution profiles of the two most promising F1 formulations, F1_HTP3 and F1_VTP2, respectively, following storage under accelerated conditions for 6 months. Note that these dissolution tests were performed by putting formulations containing equivalent to 120 mg of LUM into 1 L of 0.1N HCl solution containing 1% (w/v) SLS. The dissolution profile of the commercial product (Riamet@), obtained using the same dissolution method, is plotted as comparison references. The dashed line represents the measured saturated solubility of crystalline LUM powders in the same medium.
Figure 2. In-vitro drug dissolution profiles of the two most promising F1 formulations, F1_HTP3 and F1_VTP2, respectively, following storage under accelerated conditions for 6 months. Note that these dissolution tests were performed by putting formulations containing equivalent to 120 mg of LUM into 1 L of 0.1N HCl solution containing 1% (w/v) SLS. The dissolution profile of the commercial product (Riamet@), obtained using the same dissolution method, is plotted as comparison references. The dashed line represents the measured saturated solubility of crystalline LUM powders in the same medium.
Methods: Amorphous solid dispersions of lumefantrine with Soluplus® were prepared using hot melt extrusion. Various processing parameters, including temperature profiles and production scales, were evaluated to optimize the drug loading and physical stability. Techniques like DSC, PXRD, and in-vitro dissolution testing were employed to characterize the formulations and assess their performance.
Results: ASDs were successfully produced with different drug loadings (30% and 50% w/w LUM) and extrusion conditions. Higher processing temperatures and vertical scaled-up production improved amorphization and dissolution rates. F1 formulations with 30% w/w LUM showed superior dissolution compared to F2 with 50% w/w. Stability studies indicated some recrystallization over six months, but formulations still exhibited much better performance than commercial Riamet® tablets.
Conclusion: Vertical HME effectively improved the solubility and dissolution of LUM in Soluplus® matrices. High drug loading was achieved, but maintaining physical stability remains a challenge. The study highlights the potential of Vertical HME in developing effective anti-malarial formulations with enhanced bioavailability.
References: 1. Alhalaweh et al., 2014, Mol Pharm
2. AL-Japairai et al., 2023, Int J Pharm
3. Amin et al., 2013, Malar J
4. Armstrong et al., 2023, J Pharm Sci
5. Badman et al., 2019, J Pharm Sci
6. Bhattacharyya & Ramachandran, 2022, Materials Letters: X
7. Bhujbal et al., 2021, J Pharm Sci
8. Civati et al., 2021, Cryst Growth Des
9. de Freitas-Marques et al., 2020, J Struct Chem
10. de Margerie et al., 2021, Int J Pharm
11. Djimdé & Lefèvre, 2009, Malar J
12. Donnelly et al., 2015, Pharm Res
13. Hassan Shah et al., 2021, J Drug Deliv Sci Technol
14. Jain et al., 2017
15. Karunanithy & Muthukumarappan, 2011, Biosyst Eng
16. Kelleher et al., 2018, Int J Pharm
17. Li et al., 2016, AAPS PharmSciTech
18. Medicines for Malaria Venture, 2015
19. Meng et al., 2010, Food Research International
20. Ogutu et al., 2023, Lancet Infect Dis
21. Pawar & Shende, 2020, Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp
22. Shantanu et al., 2006, PCT/IB2006/001037
23. Su et al., 2009, International Journal of Food Engineering
24. Tian et al., 2013, Mol Pharm
25. Trasi et al., 2020, Int J Pharm X
26. Volpe-Zanutto et al., 2021, Journal of Controlled Release
27. Wahajuddin et al., 2011, Malar J
28. Weuts et al., 2003, Int J Pharm
29. World Health Organization, 2022
30. Yao et al., 2021, J Pharm Sci
31. Yenet et al., 2023, ClinicoEconomics and Outcomes Research
32. Zhou et al., 2002, J Pharm Sci
Acknowledgements: This work was supported by the following entities: The School of Pharmacy, Queen’s University Belfast; Institut Jean Lamour, Nancy, France; Rondol Industrie, Nancy, France
We acknowledge the assistance of Kemprotec Limited for providing lumefantrine and BASF Corporation for supplying Soluplus®.
No conflicts of interest were declared by the authors.
 Table 1: Nomeclature of the formulations extruded in this study.
Table 1: Nomeclature of the formulations extruded in this study. Figure 1. PXRD patterns of extruded formulations following storage under accelerated conditions (A) F1 extrudates over a 2-week period; (B) F2 extrudates over a 2-week period; (C) F1 extrudates over a 6-month period; and (D) F2 extrudates over a 6-month period. Note that the PXRD pattern of the physical mixture of each formulation is presented at the top of each diffractogram for comparison.
Figure 1. PXRD patterns of extruded formulations following storage under accelerated conditions (A) F1 extrudates over a 2-week period; (B) F2 extrudates over a 2-week period; (C) F1 extrudates over a 6-month period; and (D) F2 extrudates over a 6-month period. Note that the PXRD pattern of the physical mixture of each formulation is presented at the top of each diffractogram for comparison. Figure 2. In-vitro drug dissolution profiles of the two most promising F1 formulations, F1_HTP3 and F1_VTP2, respectively, following storage under accelerated conditions for 6 months. Note that these dissolution tests were performed by putting formulations containing equivalent to 120 mg of LUM into 1 L of 0.1N HCl solution containing 1% (w/v) SLS. The dissolution profile of the commercial product (Riamet@), obtained using the same dissolution method, is plotted as comparison references. The dashed line represents the measured saturated solubility of crystalline LUM powders in the same medium.
Figure 2. In-vitro drug dissolution profiles of the two most promising F1 formulations, F1_HTP3 and F1_VTP2, respectively, following storage under accelerated conditions for 6 months. Note that these dissolution tests were performed by putting formulations containing equivalent to 120 mg of LUM into 1 L of 0.1N HCl solution containing 1% (w/v) SLS. The dissolution profile of the commercial product (Riamet@), obtained using the same dissolution method, is plotted as comparison references. The dashed line represents the measured saturated solubility of crystalline LUM powders in the same medium.