Formulation and Delivery - Chemical
(M1130-07-41) Photonic Formulations of Hydroxypropyl Cellulose – Study of Mixtures with a Pharmaceutical Potential
Monday, October 21, 2024
11:30 AM - 12:30 PM MT

Edmont Stoyanov, PhD (he/him/his)
Global Technical Director
Nisso Chemical Europe
Dusseldorf, Nordrhein-Westfalen, Germany- AJ
Andre Jaquier
PhD student
University of Applied Sciences and Arts Northwestern Switzerland
Basel, Basel-Stadt, Switzerland - MK
Martin Kuentz, Ph.D.
Professor
University of Applied Sciences and Arts Northwestern Switzerland
Muttenz, Basel-Stadt, Switzerland - AN
Andreas Niederquell, Pharm.D. (he/him/his)
Postdoc Student
University of Applied Sciences and Arts Northwestern Switzerland
Basel, Basel-Stadt, Switzerland
Presenting Author(s)
Main Author(s)
Co-Author(s)
Purpose: Hydroxypropyl cellulose (HPC) has been widely used in pharmaceutical formulations [1] and interesting research in material science focused on the optical properties of concentrated HPC films [2] Intriguing colors of such HPC gels can be occasionally observed based on a mesophase, which may find also pharmaceutical applications. One aspect is that coloring dyes or pigments in dosage forms often raise toxicological concerns so a color based on mesoscopic structuring of a polymer would be highly attractive as an alternative. Another pharmaceutical rationale is about drug product counterfeiting because the complex iridescent appearance of such HPC formulations could make it hard to copy an originator’s drug product. Therefore, the current work explores the optical properties of first aqueous HPC gels to then proceed to research on other more complex mixtures as candidates for photonic formulations in oral pharmaceutics.
Methods: Following an initial pre-testing, main experiments (50 g) were based on a Micro Mixer (Krieger AG, Switzerland) (Figure 1A), which combined a double jacketed vessel with a stirrer for standardized mixing conditions under vacuum. HPC was kindly donated by Nisso Chemical Europe GmbH (Düsseldorf, Germany). The vessel was connected to a MA-4 heating circulator (Julabo, Germany) and following a manual mixing of the blends, the lid was closed, vacuum was set to 550 mbar and the temperature was set to 50°C with a homogenization step at 100 rpm for 30 min. Analysis of formulation appearance was based on a cardboard box with 280 mm length, 160 mm, width and 510 mm height. This created box enabled insertion of a camera (iPhone 13 Pro, Apple USA) and a standardized light source using a lamp with a Wiz colors bulb (Signify, Netherlands) in E14 format and 470 lm that was controllable via the “Wiz” software application for Android and iOS to ensure constant intensity of the light source. The box hole for the illumination lamb was equipped with a WhiteDome light diffuser (Gary Fong, USA) for homogenized light dispersion inside the box. Image cropping was based on the “Preview” application in macOS to convert each picture from DNG format to 16-bit TIFF format to maintain a good image quality. Subsequently, images were cropped for further analysis either in MATLAB (MathWorks, Natick, USA) for additive red-green-blue (RGB) calculations or PythonTM scripts were run on Visual Studio Code by Microsoft (Redmond, USA) as integrated development environment for analyzing colors in the Hue Saturation Lightness (HSL) environment (Figure 1B).
Results: First binary water- HPC mixtures were studied, and high concentrations of the cellulosic polymer indeed resulted in an iridescent color but only in a limited concentration range. Figure 2 depicts the RGB (CIE 1931) chromaticity diagram obtained, which indicates that different concentrations of HPC corresponded to distinct color locations. A separate analysis of samples in the alternative HSL color space was also interesting. Thus, the visually experienced iridescence intensity appeared to correspond to the HSL saturation value within a given color domain. In a next step, the influence of additives was studied regarding a possible enhanced iridescence in the water-based HPC gels. Different candidates were identified and Figure 3A shows the example of a green iridescence in a sample of 5% w/w glycerin added to the 60% w/w/ HPC SL gel in water. There were further mixtures studied with a low water content (i.e. 5-10%) and 30% w/w of a lipid or co-solvent. An initial screening showed with a series of lipids and co-solvents that iridescence was in such mixtures only rarely found but interesting was a mixture of 30% w/w diethylene glycol monoethyl ether with 60% w/w HPC SL and 10 % w/w water. This system had a nearly undetectable iridescence with ambient light (Figure 3B1) but once a focused local light source was applied, a clear iridescence became apparent (Figure 3B2). Such a system with a concealed iridescence could be useful as counterfeiting measure, while the mixture has potential to dissolve a poorly water-soluble drug.
Conclusion: This work addressed the phenomenon that concentrated HPC gels can form a liquid crystalline structure with an iridescent appearance. The polymeric gels were investigated for their optical properties and additives were studied regarding a possible enhancement of iridescence. Interesting mixture candidates were identified, and such novel photonic formulation may find a pharmaceutical usage either as a dye-free oral drug delivery system or in the field of counterfeiting, but more research is needed to better assess the application potential of such novel photonic formulations.
References: [1] Niederquell, A., et al., Hydroxypropyl Cellulose for Drug Precipitation Inhibition: From the Potential of Molecular Interactions to Performance Considering Microrheology. Mol. Pharm., 2022, 19, 690-703.
[2] Chan, C. L. C., Bay, M.M., Jacucci, G., Vadrucci, R., Williams, C.A., van de Kerkhof, G.T., Parker, R.M., Vynck, K., Frka-Petesic, B., Vignolini, S., Visual appearance of chiral nematic cellulose-based pho-tonic films: Angular and polarization independent color response with a twist. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1905151.
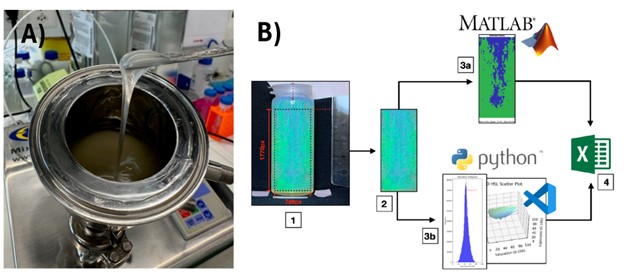 Figure 1 – A) The highly viscous HPC gels required manufacture using a micro-scale mixer that allowed processing under vacuum. B) Images of the samples were processed digitally to evaluate according to RGB or HSL, color analysis, respectively.
Figure 1 – A) The highly viscous HPC gels required manufacture using a micro-scale mixer that allowed processing under vacuum. B) Images of the samples were processed digitally to evaluate according to RGB or HSL, color analysis, respectively.
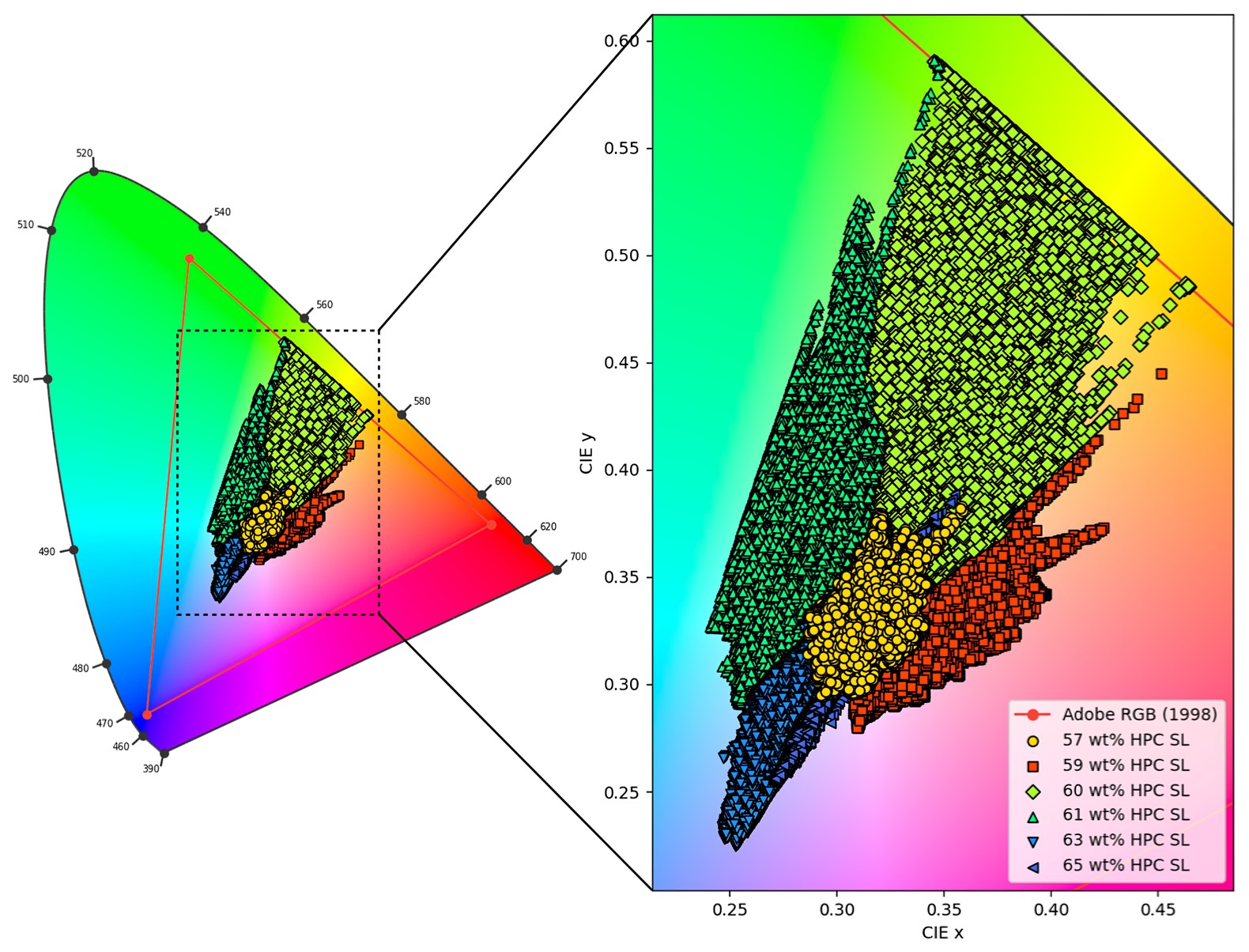 Figure 2 – Aqueous gels of HPC SL of initial trials as given in a CIE 1931 chromaticity diagram with all the plotted RGB values of the water-polymer gels with a HPC SL concentration of 57% w/w (yellow cir-cles), 59% w/w (red squares), 60% (light green diamonds), 61% w/w (upward-facing aqua green trian-gles), 63% w/w (downward-facing light blue triangles) and finally, 65% w/w (dark blue left-facing trian-gles). The triangle with red lines represents the boundary of colorations within the Adobe RGB 1998 standard gamut, which was defined during the conversion of images from DNG to TIFF format.
Figure 2 – Aqueous gels of HPC SL of initial trials as given in a CIE 1931 chromaticity diagram with all the plotted RGB values of the water-polymer gels with a HPC SL concentration of 57% w/w (yellow cir-cles), 59% w/w (red squares), 60% (light green diamonds), 61% w/w (upward-facing aqua green trian-gles), 63% w/w (downward-facing light blue triangles) and finally, 65% w/w (dark blue left-facing trian-gles). The triangle with red lines represents the boundary of colorations within the Adobe RGB 1998 standard gamut, which was defined during the conversion of images from DNG to TIFF format.
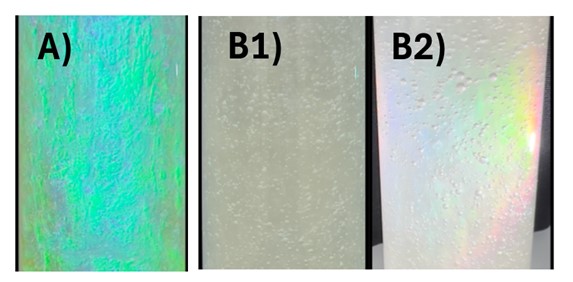 Figure 3 – A) 60% w/w HPC SL gel in 35% w/w water with 5% w/w glycerin and B1) as well as B2) are co-solvent systems with 60% w/w HPC SL, 10% w/w water and 30% diethylene glycol monoethyl ether. B2) shows the situation of a locally incoming light from the right side, which reveals a clear iridescence that is otherwise not well detected at ambient light conditions.
Figure 3 – A) 60% w/w HPC SL gel in 35% w/w water with 5% w/w glycerin and B1) as well as B2) are co-solvent systems with 60% w/w HPC SL, 10% w/w water and 30% diethylene glycol monoethyl ether. B2) shows the situation of a locally incoming light from the right side, which reveals a clear iridescence that is otherwise not well detected at ambient light conditions.
Methods: Following an initial pre-testing, main experiments (50 g) were based on a Micro Mixer (Krieger AG, Switzerland) (Figure 1A), which combined a double jacketed vessel with a stirrer for standardized mixing conditions under vacuum. HPC was kindly donated by Nisso Chemical Europe GmbH (Düsseldorf, Germany). The vessel was connected to a MA-4 heating circulator (Julabo, Germany) and following a manual mixing of the blends, the lid was closed, vacuum was set to 550 mbar and the temperature was set to 50°C with a homogenization step at 100 rpm for 30 min. Analysis of formulation appearance was based on a cardboard box with 280 mm length, 160 mm, width and 510 mm height. This created box enabled insertion of a camera (iPhone 13 Pro, Apple USA) and a standardized light source using a lamp with a Wiz colors bulb (Signify, Netherlands) in E14 format and 470 lm that was controllable via the “Wiz” software application for Android and iOS to ensure constant intensity of the light source. The box hole for the illumination lamb was equipped with a WhiteDome light diffuser (Gary Fong, USA) for homogenized light dispersion inside the box. Image cropping was based on the “Preview” application in macOS to convert each picture from DNG format to 16-bit TIFF format to maintain a good image quality. Subsequently, images were cropped for further analysis either in MATLAB (MathWorks, Natick, USA) for additive red-green-blue (RGB) calculations or PythonTM scripts were run on Visual Studio Code by Microsoft (Redmond, USA) as integrated development environment for analyzing colors in the Hue Saturation Lightness (HSL) environment (Figure 1B).
Results: First binary water- HPC mixtures were studied, and high concentrations of the cellulosic polymer indeed resulted in an iridescent color but only in a limited concentration range. Figure 2 depicts the RGB (CIE 1931) chromaticity diagram obtained, which indicates that different concentrations of HPC corresponded to distinct color locations. A separate analysis of samples in the alternative HSL color space was also interesting. Thus, the visually experienced iridescence intensity appeared to correspond to the HSL saturation value within a given color domain. In a next step, the influence of additives was studied regarding a possible enhanced iridescence in the water-based HPC gels. Different candidates were identified and Figure 3A shows the example of a green iridescence in a sample of 5% w/w glycerin added to the 60% w/w/ HPC SL gel in water. There were further mixtures studied with a low water content (i.e. 5-10%) and 30% w/w of a lipid or co-solvent. An initial screening showed with a series of lipids and co-solvents that iridescence was in such mixtures only rarely found but interesting was a mixture of 30% w/w diethylene glycol monoethyl ether with 60% w/w HPC SL and 10 % w/w water. This system had a nearly undetectable iridescence with ambient light (Figure 3B1) but once a focused local light source was applied, a clear iridescence became apparent (Figure 3B2). Such a system with a concealed iridescence could be useful as counterfeiting measure, while the mixture has potential to dissolve a poorly water-soluble drug.
Conclusion: This work addressed the phenomenon that concentrated HPC gels can form a liquid crystalline structure with an iridescent appearance. The polymeric gels were investigated for their optical properties and additives were studied regarding a possible enhancement of iridescence. Interesting mixture candidates were identified, and such novel photonic formulation may find a pharmaceutical usage either as a dye-free oral drug delivery system or in the field of counterfeiting, but more research is needed to better assess the application potential of such novel photonic formulations.
References: [1] Niederquell, A., et al., Hydroxypropyl Cellulose for Drug Precipitation Inhibition: From the Potential of Molecular Interactions to Performance Considering Microrheology. Mol. Pharm., 2022, 19, 690-703.
[2] Chan, C. L. C., Bay, M.M., Jacucci, G., Vadrucci, R., Williams, C.A., van de Kerkhof, G.T., Parker, R.M., Vynck, K., Frka-Petesic, B., Vignolini, S., Visual appearance of chiral nematic cellulose-based pho-tonic films: Angular and polarization independent color response with a twist. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1905151.
 Figure 1 – A) The highly viscous HPC gels required manufacture using a micro-scale mixer that allowed processing under vacuum. B) Images of the samples were processed digitally to evaluate according to RGB or HSL, color analysis, respectively.
Figure 1 – A) The highly viscous HPC gels required manufacture using a micro-scale mixer that allowed processing under vacuum. B) Images of the samples were processed digitally to evaluate according to RGB or HSL, color analysis, respectively. Figure 2 – Aqueous gels of HPC SL of initial trials as given in a CIE 1931 chromaticity diagram with all the plotted RGB values of the water-polymer gels with a HPC SL concentration of 57% w/w (yellow cir-cles), 59% w/w (red squares), 60% (light green diamonds), 61% w/w (upward-facing aqua green trian-gles), 63% w/w (downward-facing light blue triangles) and finally, 65% w/w (dark blue left-facing trian-gles). The triangle with red lines represents the boundary of colorations within the Adobe RGB 1998 standard gamut, which was defined during the conversion of images from DNG to TIFF format.
Figure 2 – Aqueous gels of HPC SL of initial trials as given in a CIE 1931 chromaticity diagram with all the plotted RGB values of the water-polymer gels with a HPC SL concentration of 57% w/w (yellow cir-cles), 59% w/w (red squares), 60% (light green diamonds), 61% w/w (upward-facing aqua green trian-gles), 63% w/w (downward-facing light blue triangles) and finally, 65% w/w (dark blue left-facing trian-gles). The triangle with red lines represents the boundary of colorations within the Adobe RGB 1998 standard gamut, which was defined during the conversion of images from DNG to TIFF format. Figure 3 – A) 60% w/w HPC SL gel in 35% w/w water with 5% w/w glycerin and B1) as well as B2) are co-solvent systems with 60% w/w HPC SL, 10% w/w water and 30% diethylene glycol monoethyl ether. B2) shows the situation of a locally incoming light from the right side, which reveals a clear iridescence that is otherwise not well detected at ambient light conditions.
Figure 3 – A) 60% w/w HPC SL gel in 35% w/w water with 5% w/w glycerin and B1) as well as B2) are co-solvent systems with 60% w/w HPC SL, 10% w/w water and 30% diethylene glycol monoethyl ether. B2) shows the situation of a locally incoming light from the right side, which reveals a clear iridescence that is otherwise not well detected at ambient light conditions.