Formulation and Delivery - Biomolecular
(M1530-10-59) Antimicrobial Polymer-siRNA Polyplexes as a Dual-Mode Platform for the Treatment of Wound Biofilm Infection and Inflammation Control
Monday, October 21, 2024
3:30 PM - 4:30 PM MT

Jungmi Park (she/her/hers)
Graduate Student
University of Massachusetts
Belchertown, Massachusetts, United States
Jungmi Park (she/her/hers)
Graduate Student
University of Massachusetts
Belchertown, Massachusetts, United States- TJ
Taewon Jeon, Ph.D.
Post-Doc
Massachusetts Institute of Technology
Amherst, Massachusetts, United States - JV
Jessa Marie V.Makabenta, Ph.D.
Senior R&D Chemist
Avient
Amherst, Massachusetts, United States - VR
Vincent M. Rotello, Ph.D.
Professor
University of Massachusetts
Amherst, Massachusetts, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Main Author(s)
Co-Author(s)
Purpose: Chronic non-healing wounds are a huge clinical burden, affecting 40 million patients worldwide with total spending estimates close to USD 100 billion. Most chronic wounds are attributed to biofilm infections which impede the repair of 60% of non-healing wounds. Wound healing is a dynamic process that requires an orderly transition from the inflammatory stage, progressing to tissue regeneration and, finally, tissue reorganization. Therefore, treatment of wound biofilm infections faces challenges from both pathogens and uncontrolled host immune response.
Methods: We hypothesized treating both issues through a single vector would provide enhanced wound healing as well as treating biofilm-associated infections. Here, we report using a potent cationic antimicrobial polymer to generate siRNA polyplexes for dual-mode treatment of wound biofilms tested in vitro and in vivo. We used electrostatic complementarity between a poly(oxanorborneneimide) cationic antimicrobial polymer and anionic small interfering RNA (siRNA) to generate self-assembled polyplexes. These systems combine potent antibiofilm activity with efficient delivery of immunomodulatory siRNA to generate dual-mode wound therapeutics.
Results: These polyplexes act both as an antibiofilm agent and a delivery vehicle for siRNA for the knockdown of biofilm-associated pro-inflammatory MMP9 in host macrophages. The resulting polyplexes were effective in vitro, eradicating MRSA biofilms and efficiently delivering siRNA to macrophages in vitro with concomitant knockdown of MMP9. Polyplexes were likewise effective in an in vivo murine wound biofilm model, significantly reducing bacterial load in the wound (∼99% bacterial clearance) and reducing MMP9 expression by 80% (qRT-PCR). In vivo studies demonstrated significant antimicrobial activity, decreased purulence, and significant improvement in wound healing for the polyplexes relative to the polymer alone and clinically-used vancomycin positive control.
Conclusion: In summary, we present a dual-mode antimicrobial/antiinflammatory strategy that provides a single vector system that is a promising non-surgical strategy for treating chronic non-healing wounds caused by biofilm infections. This combined approach harnesses the strengths of both antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory modalities, leveraging their disparate timeframes to optimize the host immune response and enhance the wound healing process. Overall, the integration of antimicrobial activity with immunomodulation provides new avenues for the treatment of chronic biofilm infections.
References: Jeon, T.; V. Makabenta, J. M.; Park, J.; Nabawy, A.; Anil Cicek, Y.; S. Mirza, S.; Welton, J.; Aamir Hassan, M.; Huang, R.; Mager, J.; M. Rotello, V. Antimicrobial Polymer-siRNA Polyplexes as a Dual-Mode Platform for the Treatment of Wound Biofilm Infections. Materials Horizons 2023, 10, 5500-5507
Acknowledgements: This research was supported by the National Institutes of Health under R01 AI134770 and EB022641. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Institutes of Health. Bacteria samples of methicillin-resistant S. aureus of clinical isolates from the Infectious Diseases Research Laboratory at Mayo Clinic were kindly provided by Dr. Robin Patel. The bioluminescent MRSA USA300 NRS384 strain, SAP-231, was kindly gifted by Dr. Roger Plaut. Microscopy data was obtained at the Light Microscopy Facility and Nikon Center of Excellence at the Institute for Applied Life Sciences (IALS), UMass Amherst with support from the Massachusetts Life Sciences Center. In vivo work was carried out at UMass Animal Care Facility.
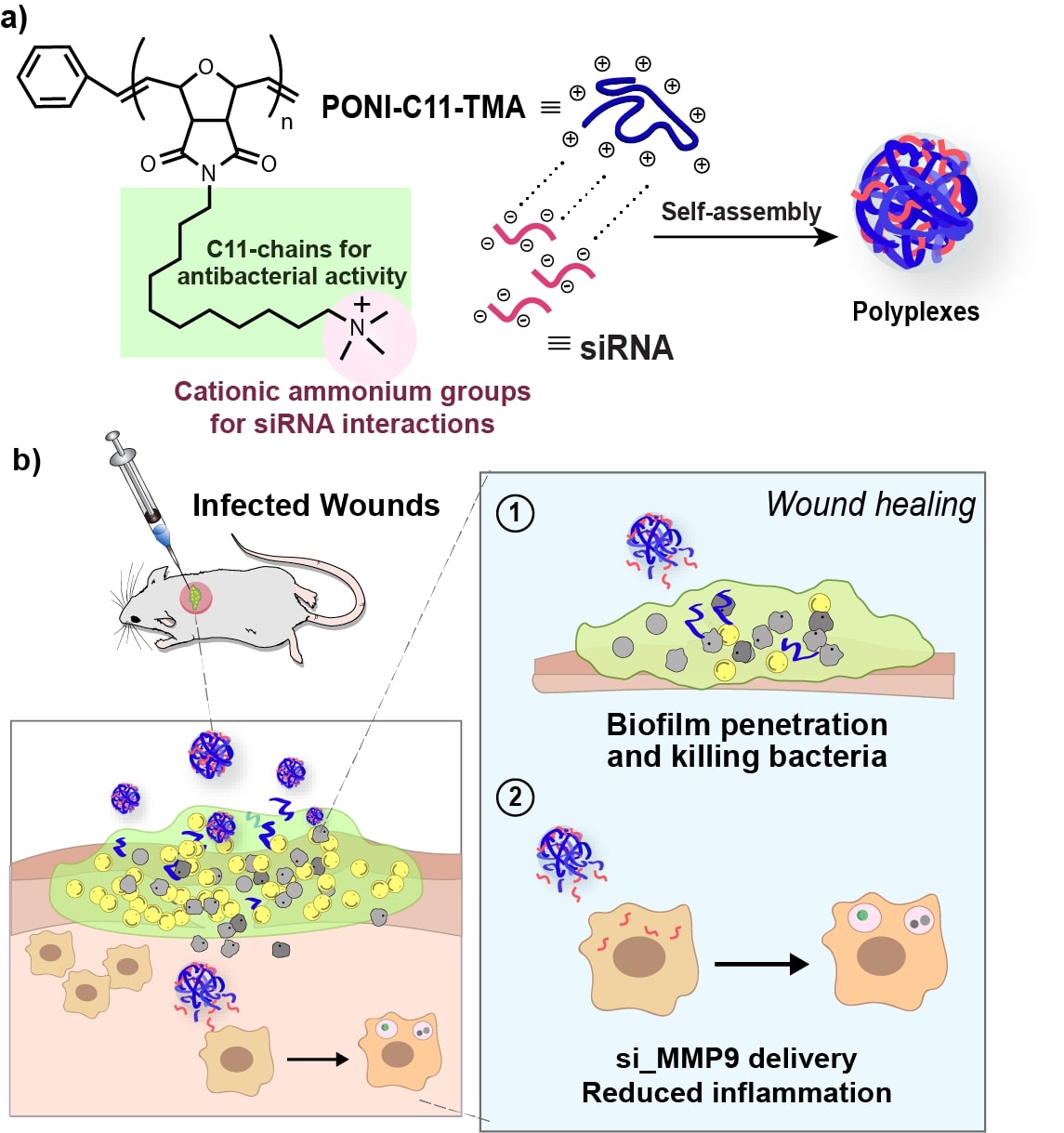 Figure 1. Schematic representation of a) engineering polyplexes via electrostatic interactions of siRNA and PONI-C11-TMA and b) in vivo treatment of polyplexes for infected wounds on mice showing efficient biofilm penetration and eradication of bacteria combined with si_MMP9 delivery strategy induced reduction in inflammation.
Figure 1. Schematic representation of a) engineering polyplexes via electrostatic interactions of siRNA and PONI-C11-TMA and b) in vivo treatment of polyplexes for infected wounds on mice showing efficient biofilm penetration and eradication of bacteria combined with si_MMP9 delivery strategy induced reduction in inflammation.
.jpg) Figure 3. Effects of polyplexes on methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA) biofilm. a) Representative 3D views of confocal image stacks of red fluorescent protein (RFP)-expressing MRSA biofilm after 1 h incubation with Cy5.5-labelled polyplexes (Cyan). Overlay images show Cy5.5-polyplexes completely penetrate the entire biofilm, interacting with MRSA cells. Biofilm thickness is ~ 18μm. b) Screening the polymer and the polyplexes formulated with different N/P ratios via their antimicrobial activity against MRSA IDRL-6169 for biocompatibility. c) Evaluating siRNA activity through MMP9 knockdown in RAW 264.7 macrophages quantified by qRT-PCR. Error bars represent the standard deviation (SD) of three experimental replicates (Data are presented as mean ± SD, one-way ANOVA, and Tukey multiple comparisons, ****p < 0.001). and fluorescent reporter gene silencing and evaluation of siRNA activity. d) Representative confocal microscopy images of cells after treatment with PONI-C11-TMA/si_eGFP polyplexes. Cell nuclei stained with DAPI (Blue). Deliveries were performed with polyplexes formulated at N/P 40 ratio with 100 nM of siRNA. Scale bar: 50 μm.
Figure 3. Effects of polyplexes on methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA) biofilm. a) Representative 3D views of confocal image stacks of red fluorescent protein (RFP)-expressing MRSA biofilm after 1 h incubation with Cy5.5-labelled polyplexes (Cyan). Overlay images show Cy5.5-polyplexes completely penetrate the entire biofilm, interacting with MRSA cells. Biofilm thickness is ~ 18μm. b) Screening the polymer and the polyplexes formulated with different N/P ratios via their antimicrobial activity against MRSA IDRL-6169 for biocompatibility. c) Evaluating siRNA activity through MMP9 knockdown in RAW 264.7 macrophages quantified by qRT-PCR. Error bars represent the standard deviation (SD) of three experimental replicates (Data are presented as mean ± SD, one-way ANOVA, and Tukey multiple comparisons, ****p < 0.001). and fluorescent reporter gene silencing and evaluation of siRNA activity. d) Representative confocal microscopy images of cells after treatment with PONI-C11-TMA/si_eGFP polyplexes. Cell nuclei stained with DAPI (Blue). Deliveries were performed with polyplexes formulated at N/P 40 ratio with 100 nM of siRNA. Scale bar: 50 μm.
.jpg) In vivo therapeutic efficacy of PONI-C11-TMA/siRNA polyplexes for severe wound biofilm infections. a) Schematic representation of the murine model of wound biofilm infection. b) SEM image of mice skin sample confirming biofilm formation at the wound site. Scale bar: 5 μm. c) Bioluminescence signals from the wound area of representative mice on the different days of treatment. d) Extent of bacterial reduction relative to negative control, PBS only [bacteria reduction = (log CFU count)PBS - (log CFU count)treatment group]. Error bars represent the mean ± the standard error of the mean (SEM) (n=4, one-way ANOVA and Tukey multiple comparisons, *p < 0.05). e) In vivo treatment of PONI-C11-TMA/si_MMP9 decreased MMP9 mRNA levels quantified by qRT-PCR. Error bars represent the mean ± the standard error of the mean (SEM) (n=4, one-way ANOVA and Tukey multiple comparisons, ***p < 0.001. f) Degree of wound size reduction at the day of sacrifice relative to the first day of treatment. One-way ANOVA and Tukey multiple comparisons, *, **, *** indicate p-value < 0.05, 0.01 or 0.001, respectively.
In vivo therapeutic efficacy of PONI-C11-TMA/siRNA polyplexes for severe wound biofilm infections. a) Schematic representation of the murine model of wound biofilm infection. b) SEM image of mice skin sample confirming biofilm formation at the wound site. Scale bar: 5 μm. c) Bioluminescence signals from the wound area of representative mice on the different days of treatment. d) Extent of bacterial reduction relative to negative control, PBS only [bacteria reduction = (log CFU count)PBS - (log CFU count)treatment group]. Error bars represent the mean ± the standard error of the mean (SEM) (n=4, one-way ANOVA and Tukey multiple comparisons, *p < 0.05). e) In vivo treatment of PONI-C11-TMA/si_MMP9 decreased MMP9 mRNA levels quantified by qRT-PCR. Error bars represent the mean ± the standard error of the mean (SEM) (n=4, one-way ANOVA and Tukey multiple comparisons, ***p < 0.001. f) Degree of wound size reduction at the day of sacrifice relative to the first day of treatment. One-way ANOVA and Tukey multiple comparisons, *, **, *** indicate p-value < 0.05, 0.01 or 0.001, respectively.
Methods: We hypothesized treating both issues through a single vector would provide enhanced wound healing as well as treating biofilm-associated infections. Here, we report using a potent cationic antimicrobial polymer to generate siRNA polyplexes for dual-mode treatment of wound biofilms tested in vitro and in vivo. We used electrostatic complementarity between a poly(oxanorborneneimide) cationic antimicrobial polymer and anionic small interfering RNA (siRNA) to generate self-assembled polyplexes. These systems combine potent antibiofilm activity with efficient delivery of immunomodulatory siRNA to generate dual-mode wound therapeutics.
Results: These polyplexes act both as an antibiofilm agent and a delivery vehicle for siRNA for the knockdown of biofilm-associated pro-inflammatory MMP9 in host macrophages. The resulting polyplexes were effective in vitro, eradicating MRSA biofilms and efficiently delivering siRNA to macrophages in vitro with concomitant knockdown of MMP9. Polyplexes were likewise effective in an in vivo murine wound biofilm model, significantly reducing bacterial load in the wound (∼99% bacterial clearance) and reducing MMP9 expression by 80% (qRT-PCR). In vivo studies demonstrated significant antimicrobial activity, decreased purulence, and significant improvement in wound healing for the polyplexes relative to the polymer alone and clinically-used vancomycin positive control.
Conclusion: In summary, we present a dual-mode antimicrobial/antiinflammatory strategy that provides a single vector system that is a promising non-surgical strategy for treating chronic non-healing wounds caused by biofilm infections. This combined approach harnesses the strengths of both antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory modalities, leveraging their disparate timeframes to optimize the host immune response and enhance the wound healing process. Overall, the integration of antimicrobial activity with immunomodulation provides new avenues for the treatment of chronic biofilm infections.
References: Jeon, T.; V. Makabenta, J. M.; Park, J.; Nabawy, A.; Anil Cicek, Y.; S. Mirza, S.; Welton, J.; Aamir Hassan, M.; Huang, R.; Mager, J.; M. Rotello, V. Antimicrobial Polymer-siRNA Polyplexes as a Dual-Mode Platform for the Treatment of Wound Biofilm Infections. Materials Horizons 2023, 10, 5500-5507
Acknowledgements: This research was supported by the National Institutes of Health under R01 AI134770 and EB022641. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Institutes of Health. Bacteria samples of methicillin-resistant S. aureus of clinical isolates from the Infectious Diseases Research Laboratory at Mayo Clinic were kindly provided by Dr. Robin Patel. The bioluminescent MRSA USA300 NRS384 strain, SAP-231, was kindly gifted by Dr. Roger Plaut. Microscopy data was obtained at the Light Microscopy Facility and Nikon Center of Excellence at the Institute for Applied Life Sciences (IALS), UMass Amherst with support from the Massachusetts Life Sciences Center. In vivo work was carried out at UMass Animal Care Facility.
 Figure 1. Schematic representation of a) engineering polyplexes via electrostatic interactions of siRNA and PONI-C11-TMA and b) in vivo treatment of polyplexes for infected wounds on mice showing efficient biofilm penetration and eradication of bacteria combined with si_MMP9 delivery strategy induced reduction in inflammation.
Figure 1. Schematic representation of a) engineering polyplexes via electrostatic interactions of siRNA and PONI-C11-TMA and b) in vivo treatment of polyplexes for infected wounds on mice showing efficient biofilm penetration and eradication of bacteria combined with si_MMP9 delivery strategy induced reduction in inflammation..jpg) Figure 3. Effects of polyplexes on methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA) biofilm. a) Representative 3D views of confocal image stacks of red fluorescent protein (RFP)-expressing MRSA biofilm after 1 h incubation with Cy5.5-labelled polyplexes (Cyan). Overlay images show Cy5.5-polyplexes completely penetrate the entire biofilm, interacting with MRSA cells. Biofilm thickness is ~ 18μm. b) Screening the polymer and the polyplexes formulated with different N/P ratios via their antimicrobial activity against MRSA IDRL-6169 for biocompatibility. c) Evaluating siRNA activity through MMP9 knockdown in RAW 264.7 macrophages quantified by qRT-PCR. Error bars represent the standard deviation (SD) of three experimental replicates (Data are presented as mean ± SD, one-way ANOVA, and Tukey multiple comparisons, ****p < 0.001). and fluorescent reporter gene silencing and evaluation of siRNA activity. d) Representative confocal microscopy images of cells after treatment with PONI-C11-TMA/si_eGFP polyplexes. Cell nuclei stained with DAPI (Blue). Deliveries were performed with polyplexes formulated at N/P 40 ratio with 100 nM of siRNA. Scale bar: 50 μm.
Figure 3. Effects of polyplexes on methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA) biofilm. a) Representative 3D views of confocal image stacks of red fluorescent protein (RFP)-expressing MRSA biofilm after 1 h incubation with Cy5.5-labelled polyplexes (Cyan). Overlay images show Cy5.5-polyplexes completely penetrate the entire biofilm, interacting with MRSA cells. Biofilm thickness is ~ 18μm. b) Screening the polymer and the polyplexes formulated with different N/P ratios via their antimicrobial activity against MRSA IDRL-6169 for biocompatibility. c) Evaluating siRNA activity through MMP9 knockdown in RAW 264.7 macrophages quantified by qRT-PCR. Error bars represent the standard deviation (SD) of three experimental replicates (Data are presented as mean ± SD, one-way ANOVA, and Tukey multiple comparisons, ****p < 0.001). and fluorescent reporter gene silencing and evaluation of siRNA activity. d) Representative confocal microscopy images of cells after treatment with PONI-C11-TMA/si_eGFP polyplexes. Cell nuclei stained with DAPI (Blue). Deliveries were performed with polyplexes formulated at N/P 40 ratio with 100 nM of siRNA. Scale bar: 50 μm. .jpg) In vivo therapeutic efficacy of PONI-C11-TMA/siRNA polyplexes for severe wound biofilm infections. a) Schematic representation of the murine model of wound biofilm infection. b) SEM image of mice skin sample confirming biofilm formation at the wound site. Scale bar: 5 μm. c) Bioluminescence signals from the wound area of representative mice on the different days of treatment. d) Extent of bacterial reduction relative to negative control, PBS only [bacteria reduction = (log CFU count)PBS - (log CFU count)treatment group]. Error bars represent the mean ± the standard error of the mean (SEM) (n=4, one-way ANOVA and Tukey multiple comparisons, *p < 0.05). e) In vivo treatment of PONI-C11-TMA/si_MMP9 decreased MMP9 mRNA levels quantified by qRT-PCR. Error bars represent the mean ± the standard error of the mean (SEM) (n=4, one-way ANOVA and Tukey multiple comparisons, ***p < 0.001. f) Degree of wound size reduction at the day of sacrifice relative to the first day of treatment. One-way ANOVA and Tukey multiple comparisons, *, **, *** indicate p-value < 0.05, 0.01 or 0.001, respectively.
In vivo therapeutic efficacy of PONI-C11-TMA/siRNA polyplexes for severe wound biofilm infections. a) Schematic representation of the murine model of wound biofilm infection. b) SEM image of mice skin sample confirming biofilm formation at the wound site. Scale bar: 5 μm. c) Bioluminescence signals from the wound area of representative mice on the different days of treatment. d) Extent of bacterial reduction relative to negative control, PBS only [bacteria reduction = (log CFU count)PBS - (log CFU count)treatment group]. Error bars represent the mean ± the standard error of the mean (SEM) (n=4, one-way ANOVA and Tukey multiple comparisons, *p < 0.05). e) In vivo treatment of PONI-C11-TMA/si_MMP9 decreased MMP9 mRNA levels quantified by qRT-PCR. Error bars represent the mean ± the standard error of the mean (SEM) (n=4, one-way ANOVA and Tukey multiple comparisons, ***p < 0.001. f) Degree of wound size reduction at the day of sacrifice relative to the first day of treatment. One-way ANOVA and Tukey multiple comparisons, *, **, *** indicate p-value < 0.05, 0.01 or 0.001, respectively. 